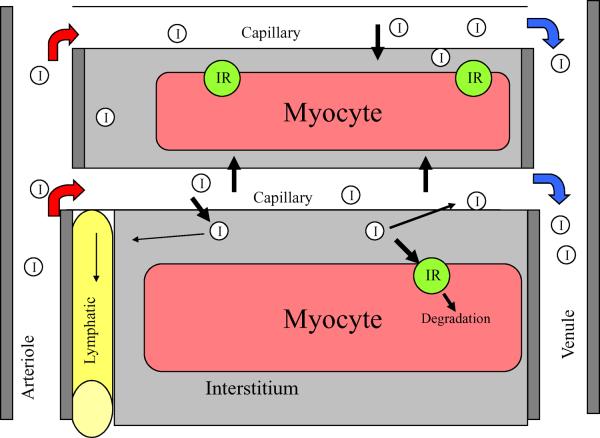
Fig. 2.
A microvascular unit within muscle is composed of a terminal arteriole that feeds 12-20 capillaries and a draining vein. The capillary is the principal site of nutrient/hormone exchange between the muscle interstitium and blood. For insulin (I), the fraction that enters muscle interstitium may either be returned to the systemic circulation, through lymphatic drainage through reverse movement back across the EC (against a concentration gradient), or be taken up by the myocyte. via the insulin receptor (IR) and ultimately degraded