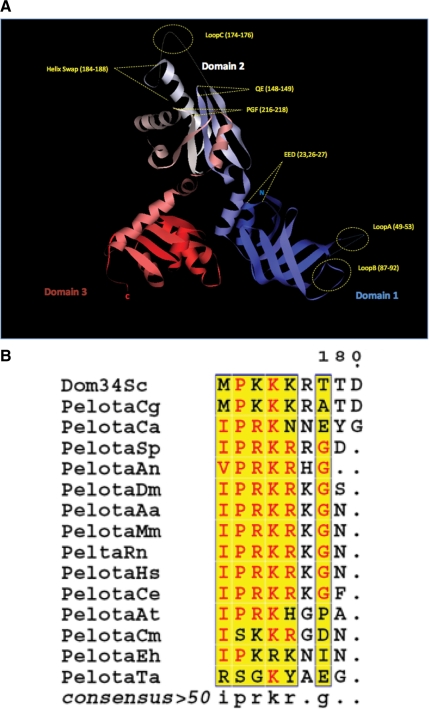
Figure 1.
(A) Ribbon diagram of the crystal structure of S. cerevisiae Dom34, highlighting the location of each mutant used in this study. Domain 1 (blue) contains the mutants loop A, loop B, and EED. Domain 2 (white) includes the mutants QE, NLS, loop C and PGF. Domain 3 is shown in red. The N- and C- termini are also represented as N and C. (B) Alignment of dom34 homology proteins from different organisms shows a cluster with highly conserved basic residues (NLS). The alignment was processed using the network protein sequence analysis (NPS) at http://npsa-pbil.ibcp.fr/ (Combet et al., 2000). The following organisms were used: S. cerevisiae (Sc); Candida glabrata (Cg); Candida albicans (Ca); Drosophila melanogaster (Dm); Aedes aegypti (Aa); Homo sapiens (Hs); Mus musculus (Mm); Rattus norvegicus (Rn); Caenorhabditis elegans (Ce); Arabidopsis thaliana (At); Schizosaccharomyces pombe (Sp); Aspergillus niger (An); Plasmodium falciparum (Pf); Toxoplasma gondii (Tg); Cryptosporidium muris (Cm); Entamoeba histolytica (Eh); Thermoplasma acidophilum (Ta).