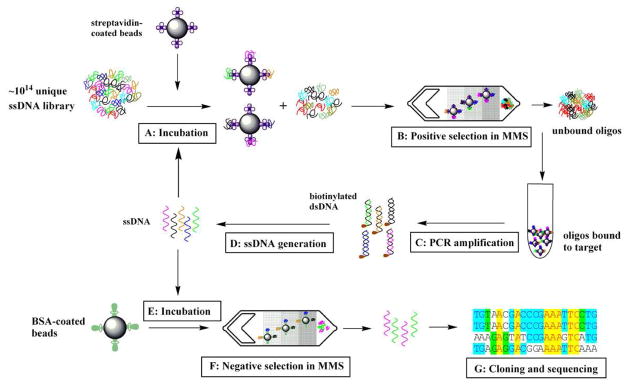
Figure 2. Microfluidic SELEX process using the MMS device.
A)Incubation of the bead-immobilized target protein with ssDNA library in binding buffer. To ensure highly stringent binding conditions, the ratio between ssDNA and the protein ratio was kept at 100:1. B) Positive selection of target-bound aptamers. The magnetic beads carrying the target protein and target-bound aptamers are trapped at the nickel patterns within the microchannel. After highly stringent washing, the external magnets are removed, and the beads are eluted into a collection vessel. C) PCR amplification of selected aptamers. The forward primer is Alexa 488-labeled for fluorescence measurements, and the reverse primer is biotinylated for ssDNA isolation. D) Single stranded DNA generation. The biotin-labeled double-stranded PCR product was incubated with Dynabeads® MyOne™ Streptavidin C1 beads for 2 hr at room temperature to separate the ds-DNA from the PCR reaction mixture. Single-stranded DNA was then generated in solution by incubating the beads with 15 mM NaOH for 4 min at room temperature. The supernatant was collected and neutralized with 1 M HCl. E) The positively selected aptamer pool is incubated with BSA-coated magnetic beads. The [BSA]/[ssDNA] ratio is 1:1. F) Negative selection in the MMS device. The unbound ssDNA fraction is collected. G) Cloning and sequencing of the isolated aptamers.