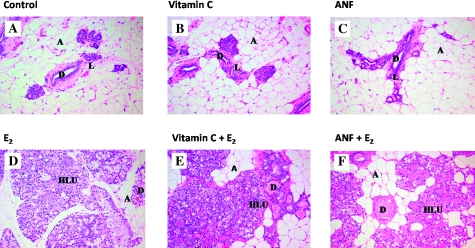
Fig. 1.
Mammary tissue from the E2, E2 + vitamin C, E2 + ANF and their respective control groups (i.e. cholesterol, cholesterol + vitamin C and cholesterol + ANF) after 240 days. Female ACI rats were treated with E2, E2 + vitamin C or E2 + ANF for 240 days. Animals in the E2, E2 + vitamin C and E2 + ANF groups were implanted with E2 pellets (subcutaneous, 3 mg E2 + 17 mg cholesterol) for 240 days. Control rats were implanted with pellets containing 17 mg cholesterol only. Vitamin C-treated rats received vitamin C (1%) in drinking water and ANF-treated rats were given ANF via diet (0.2% in food). (A–C) The mammary glands of ACI rats exposed to cholesterol, cholesterol + vitamin C or cholesterol + ANF show normal lobular architecture (L) with branched ducts (D) and normal distribution of fat/adipose tissue (A) (all panels ×100). (D–F) Mammary glands from rats in the E2, vitamin C + E2 and ANF + E2 groups show increased proliferation with dilated ducts containing inspissated secretions (D) and increased proliferation and expansion of terminal lobular units (HLU) accompanied by compression of and expansion into the surrounding fat/adipose tissue (A) (all panels ×100).