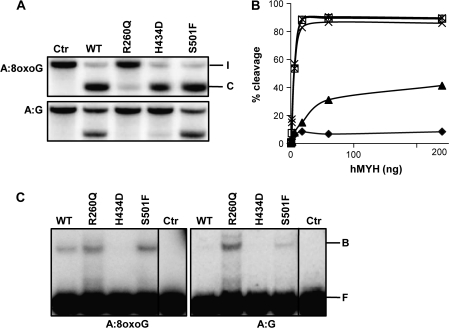
Fig. 2.
Analysis of hMYH variants. (A) Adenine DNA glycosylase activities of hMYH WT, R260Q, H434D and S501F variants were measured by incubating the respective proteins (18 ng) with a duplex oligodeoxyribonucleotide containing a single A:8oxoG or A:G basepair at 37°C for 30 min. Strand cleavage after NaOH treatment was analyzed by 20% polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and phosphorimaging (I = intact strand and C = cleavage product). (B) Different amounts (0.6–240 ng) of hMYH WT (□), R260Q (▴), H434D (X) and S501F (*) were assayed for A:8oxoG DNA glycosylase activities and percentage strand cleavage quantified with ImageQuant. Extract from Escherichia coli cells expressing empty vector and purified similarly as hMYH was used to measure the background level (⧫). (C) DNA binding properties of hMYH WT, R260Q, H434D and S501F (24 ng) to substrates containing A:8oxoG (left panel) or A:G (right panel). After incubation on ice, DNA–protein complexes (B = bound substrate) were separated from free DNA (F) by 10% native polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Control lanes were without addition of protein.