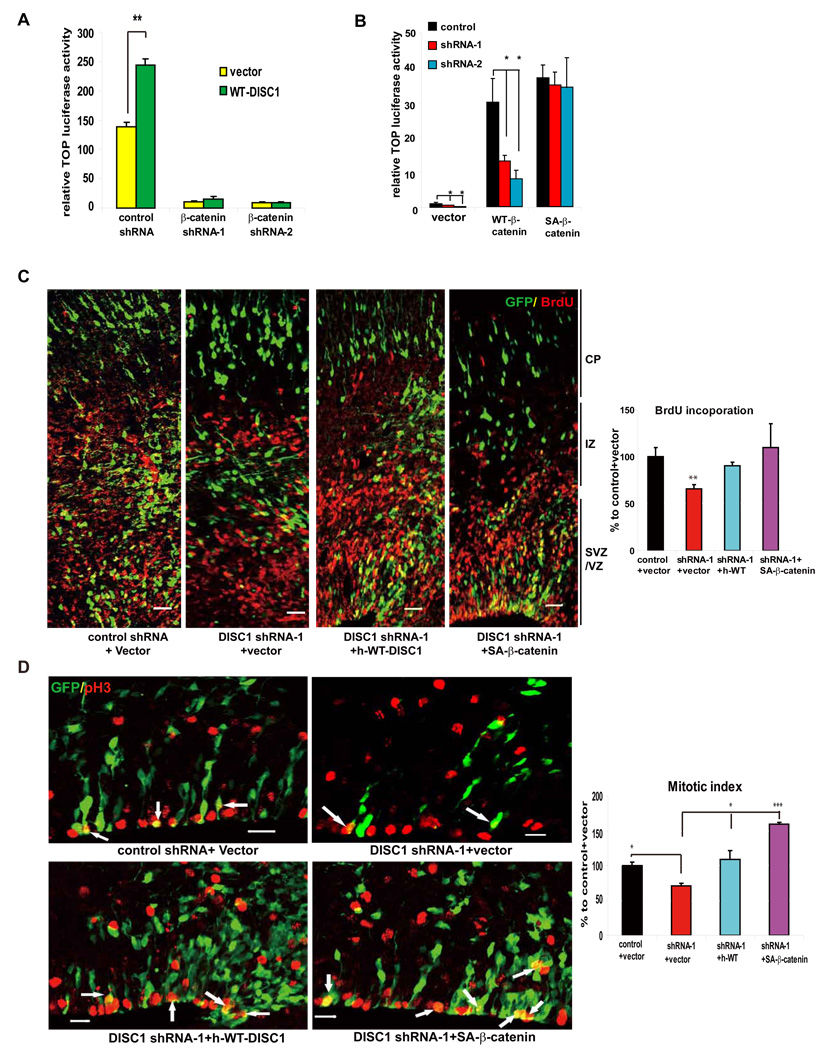
Figure 4. Stable β-catenin rescues DISC1-induced defects.
(A) Enhancement of TOP activity by DISC1 overexpression is abolished by β-catenin shRNAs in embryonic primary progenitors (n=6, p<0.01).
(B) Vector, WT-β-catenin, or SA-β-catenin was cotransfected with the TOP reporter into embryonic progenitors transduced with lentiviruses expressing DISC1 shRNAs. Only SA-β-catenin rescued the TOP activation defect in DISC1 knockdown cells (n=4, *p<0.05, **p<0.01).
(C) Cell positioning and BrdU incorporation defects caused by DISC1 loss-of-function are rescued by human WT-DISC1 or SA-β-catenin. The GFP positive cells that are also BrdU positive cells is shown as the percentage to control plus vector (n=5, **, p<0.01; ***, p<0.005). Scale bar=20 µm.
(D) The reduction in mitotic index caused by DISC1 knockdown in embryonic brains is rescued by human WT-DISC1 or SA-β-catenin. Arrows indicate GFP and pH3 double positive cells. The GFP positive cells that are also pH3 positive cells is shown as the percentage to control plus vector (n=4, *, p<.0.05; ***, p<0.005). Scale bar=20 µm.