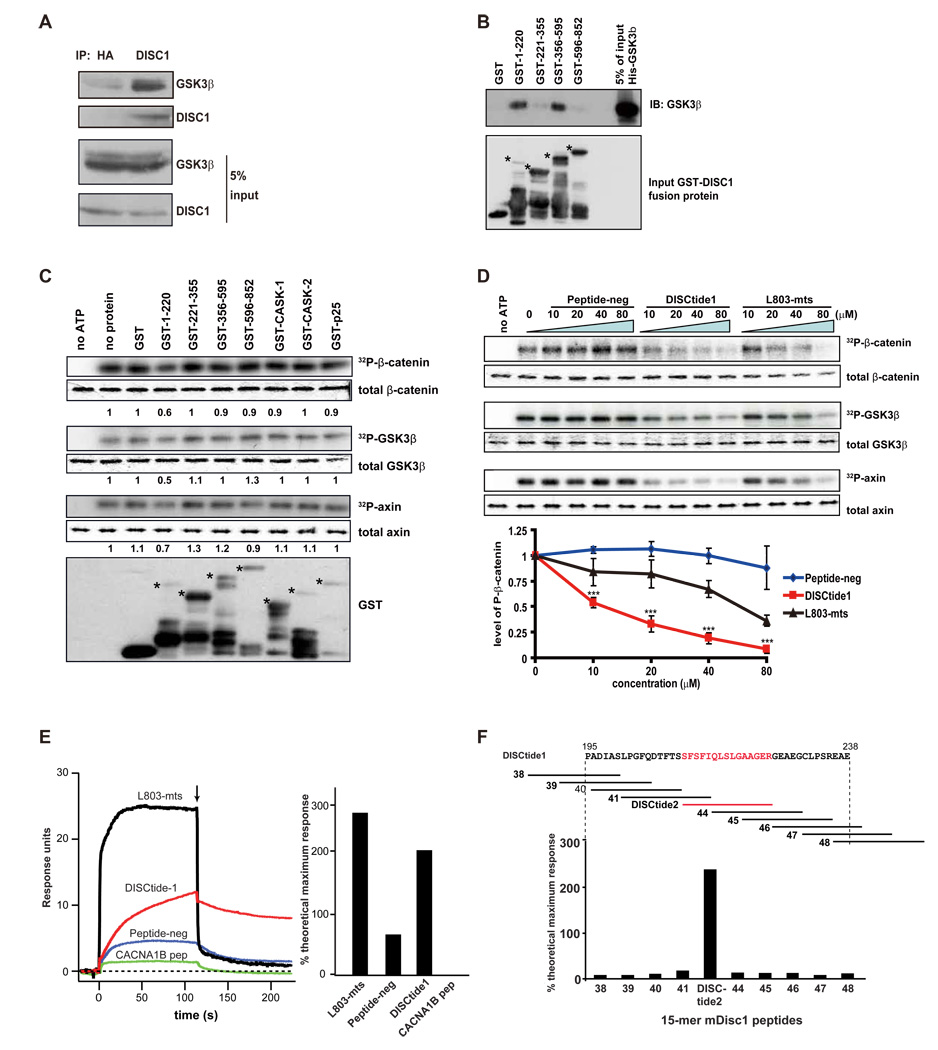
Figure 6. DISC1 regulates the GSK3β signaling pathway.
(A) DISC1 interacts with endogenous GSK3β. E14 brain lysate was subjected to immunoprecipitation with anti-HA (negative control) or anti-DISC1 antibody and immunoblotted with anti-GSK3β or DISC1 antibody.
(B) GSK3β directly binds to DISC1 in vitro. Purified His-GSK3β interacts directly with DISC1 fragments 1–220aa and 356–595aa. Stars indicate the intact GST fusion proteins.
(C) GSK3β activity is reduced by DISC1 GST-fragments in vitro. Numbers in the panel indicate the relative intensity of the band compared to the no protein lane (n=3). Stars indicate the different intact GST fusion proteins.
(D) Inhibition of GSK3β activity by DISC1 peptide 1(195–238aa) is dose-dependent. The dose-response curve is shown (n=3, ***, p<0.005).
(E) Disctide-1(195–238aa) directly binds to GSK3β Surface plasmon resonance sensorgrams for GSK3β binding assays with peptide-neg, Disctide-1, L803-mts, and a peptide from CACNA1B are shown in the left panel. The arrow indicates the injection of buffer without compound. The percent theoretical maximal response is summarized in the right hand panel for these SPR experiments.
(F) Disctide2 (211–225aa) directly binds to GSK3β The schematic shows Disctide1 (mDisc aa 195–238). Each numbered line represents a 15-mer peptide (i.e. peptide2–38 – - 48) that corresponds to the DISC1 amino acids above it. The percent theoretical maximal response for SPR binding assays at 25 µM between (Disctide1 15-mers and GSK3β is summarized at the bottom of the panel. Disctide2, indicated in red, was found to bind to GSK3β.