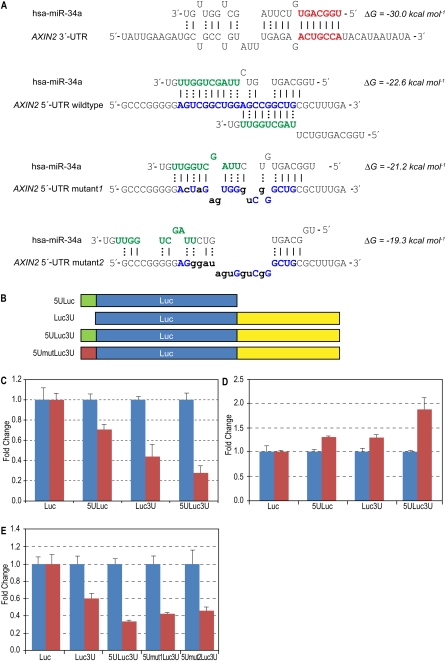
Figure 2.
Human miRNA hsa-miR-34a and target AXIN2. (A) Predicted interactions between hsa-miR-34a and AXIN2 UTR sequences. Extended seed match between the 5′-end of miR-34a and one of the 3′-UTR binding sites is shown in bold red. All predicted 3′-UTR sites are marked in the Supplemental material. Overlapping interactions between the 3′-end of miR-34a and the 5′-UTR inserted sequences are shown in bold blue. Energy was calculated using RNAhybrid. (B) Schematic showing vector constructs containing firefly luciferase reporter gene used in transfection experiments. The 5′-UTR and 3′-UTR inserts are indicated as 5U and 3U, respectively. (C) Luciferase expression fold change with miR-34a (red bars) normalized with negative control RNA oligo (blue bars). Firefly luciferase protein expression was normalized with Renilla luciferase protein. (D) Reporter constructs were co-transfected with anti-miR-34a oligo (red bars, Ambion, product ID, AM11030) and normalized with negative control RNA oligo (blue bars). (E) Effect of mutations in the 5′-UTR site—luciferase protein levels when reporter constructs were co-transfected with miR-34a (red bars) or negative control (blue bars). Error bars in panels C–E represent standard deviation from triplicate experiments.