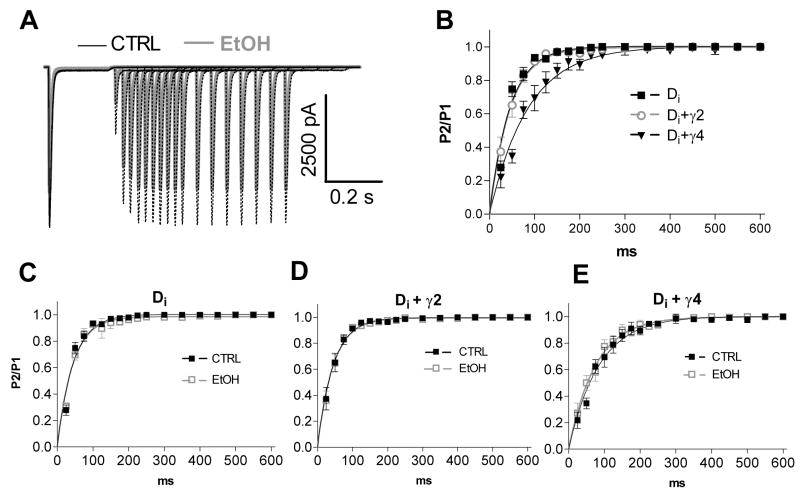
Fig. 4.
Recovery from desensitization in the presence of 100 mM ethanol. (A) Overlapping traces show the responses of GluR-Di receptors to two 200-ms pulses of 10-mM glutamate with variable intervals in the absence and presence of 100 mM ethanol (EtOH). (B) Recovery from desensitization of GluR-Di receptors with and without co-expression of TARPs. The plot shows the amplitude of the peak current of the second pulse relative to the amplitude of the peak current of the first pulse (P2/P1) as a function of pulse interval. The GluR-Di+γ4 receptors had slower recovery than the other receptors. The data for GluR-Di receptor alone (C), GluR-Di+γ2 (D) and GluR-Di+γ4 (E) in the absence and presence of 100 mM ethanol indicate that ethanol did not affect the recovery from desensitization. (n = 5–7)