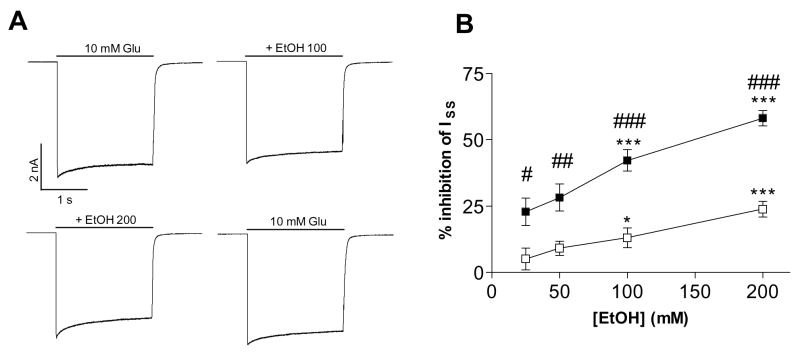
Fig. 5.
Ethanol inhibition of L505Y point-mutated GluR-Di receptor. (A) The extent of desensitization is markedly decreased in L505Y receptors as compared to wild-type GluR-Di, as can be seen from the representative recording traces. Horizontal bar indicates the 10 mM glutamate application in the absence and presence of 100 mM ethanol. (B) The steady-state currents of L505Y receptors (□) are less sensitive to EtOH than those of wild-type GluR-Di receptors (■). Repeated measures ANOVA: F1,9 = 7.8, p < 0.05. # p < 0.05, ## p < 0.01, ### p < 0.001 for the significance of the difference in ethanol inhibition between the wild-type and point-mutant L505Y GluR-Di receptors (Bonferroni test). * p < 0.05, *** p < 0.001 for the significance of the difference between the each ethanol concentration and control current (Dunnett’s test). (n = 8 for L505Y and 10–12 for wild-type)