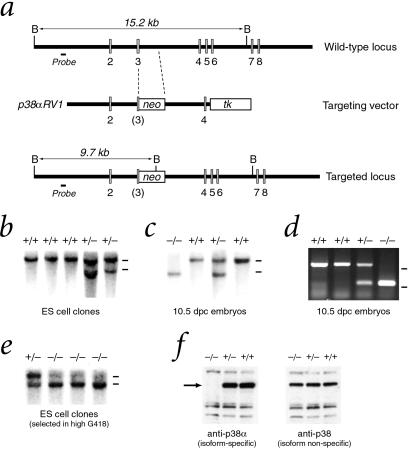
Figure 1.
Targeted disruption of the p38α gene. (a) The gene-targeting vector p38αRV1 inserts an antisense PGK–neo cassette into an EcoRI site in exon 3 and contains a 5′ flanking 4.5-kilobase (kb) EcoRI fragment and a 3′ flanking 3-kb SmaI–KpnI fragment, resulting in deletion of the 3′ half of exon 3 and part of intron 3. (b) Southern blot analysis of ES cell clones with a unique 5′ genomic probe distinguishes a wild-type 15.2-kb BamHI fragment from a 9.7-kb BamHI fragment generated by the targeted allele. Bars at right indicate positions of 15-kb wild-type and 10-kb targeted alleles. (c) Southern analysis of genomic DNA digested with BamHI from 10.5 dpc embryos obtained from a p38α heterozygous intercross. (d) PCR analysis of genomic DNA from visceral yolk sacs of 10.5 dpc embryos from a p38α heterozygous intercross. Bars at right indicate positions of markers at 500 and 250 bp. (e) Southern analysis of ES cell clones selected after growth in high concentrations (1 mg/ml) of G418 to obtain homozygosity for the p38α targeted allele. (f) Western analysis of total protein lysates from wild-type and targeted ES cells with antibodies that are specific for p38α or that crossreact with multiple p38 MAPK isoforms.