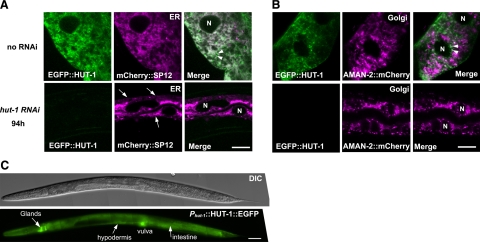
Figure 5.
HUT-1 localizes to the ER and part of the Golgi in the intestine and is required for normal ER morphology. A, B) Confocal micrographs of intestinal cells expressing EGFP::HUT-1 and the ER marker mCHERRY::SP12 (A) and the Golgi apparatus marker AMAN-2::mCHERRY (B). Nuclei are indicated by “N.” A) Top: EGFP::HUT-1 colocalized with the ER marker as well as distributed as small particles adjacent to the ER. Some of these particles are indicated by arrowheads. Bottom: knockdown of hut-1 by RNAi led to aggregation and resulted in abnormal ER network morphology resembling thin ropes or strings (arrows). B) Top: EGFP::HUT-1 partially colocalized with the Golgi apparatus marker (arrowheads). EGFP::HUT-1 tended to be detected as small particles when coexpressed with AMAN-2::mCHERRY for unknown reason. Bottom: no apparent alteration in the Golgi apparatus marker was observed with hut-1 RNAi. C) Representative DIC and fluorescent images of HUT-1::EGFP under the control of hut-1 promoter show expression in an L4 larva. Scale bars = 10 μm (A); 50 μm (B, C).