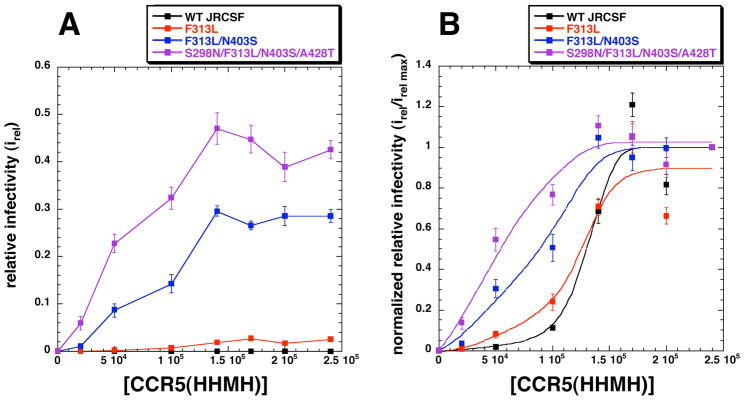
Fig 4.
Relationship of CCR5(HHMH) concentrations and viral infectivities. (A) Infectivities of wild-type and CCR5(HHMH)-adapted viruses in a HeLa-CD4 panel expressing distinct amounts of CCR5(HHMH). The infectivities of HIV-gpt viruses pseudotyped with wild-type envelopes or envelopes with the adaptive mutations designated in the figure were tested. Relative infectivities compared to JC.53 cells were plotted versus CCR5(HHMH) concentrations. The data represents the average of three independent experiments performed in triplicate. Error bars are S.E.M. (B) Normalization of the infectivity data in panel A to irel max values. The infectivity data for each virus was normalized to its maximum value, and the curves were drawn using Kaleidagraph (version 3.6) employing the least squares method. The infectivity data for wild-type virus with low titers on CCR5(HHMH) cells were easily measured using concentrated virus samples (average colony numbers on the highest expressing CCR5(HHMH) cell line ranged from 30 to 70 per well at a 1/5 virus dilution).