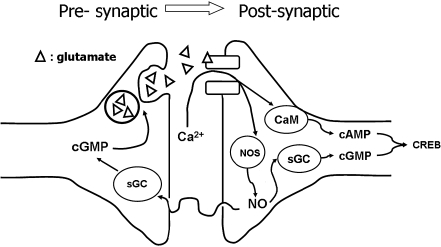
Fig. 1.
Ca2+ entry through the postsynaptic ionotropic NMDA receptor triggers LTP induction. Ca2+ results in the activation of CaMKII (a specific form of CaMK). Activated CaMKII stimulates the insertion into the membrane of the ionotropic AMPA receptor, which is involved in regular signal transduction through the generation of excitatory postsynaptic potentials. In addition, CaMKII activates AC resulting in the production of the second messenger cAMP. The latter activates PKA, which has a positive effect on the transcription factor CREB (via MAP kinases possibly). CREB activation is known to result in an increased gene expression, including the genes for AMPA receptors and thus future signal transduction is enhanced. Ca2+ is also known to activate the enzyme NOS, which produces NO. The latter can activate GC, which produces the second messenger cGMP. There are indications that, postsynaptically, cGMP has similar effects as cAMP, but via the activation of PKG. NO is also known to act as a retrograde messenger and can thus stimulate presynaptic GC. It has been found that cGMP stimulates the synthesis and release of glutamate via PKG