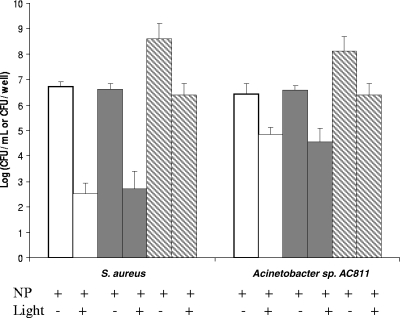
FIG. 4.
Biofilm killing assay with MB-PAA-DNP and red light illumination. Biofilms of S. aureus and Acinetobacter sp. strain AC811 were developed in a 96-well microtiter plate for 24 h. Planktonic cells (□) and dispersed biofilm cells (░⃞) were adjusted to ∼106 cells per ml in 0.45% saline solution with 5 mg of MB-PAA-DNP/ml. The mixtures were exposed to red light with a light irradiance of 38 mW/cm2 and a light fluence of 68.4 J/cm2. After eradication, serial 10-fold dilutions were plated on LB plates for colony counts. The same biofilms developed with 5 mg of MB-PAA-DNP/ml (▧) were exposed to red light with a light irradiance of 38 mW/cm2 and a light fluence of 68.4 J/cm2 after the suspension was removed. The biofilm cells were resuspended in 1 ml of 0.45% saline solution and dispersed by using homogenization, and serial 10-fold dilutions were plated onto LB plates for colony counts. Error bars indicate the standard errors of three replicates.