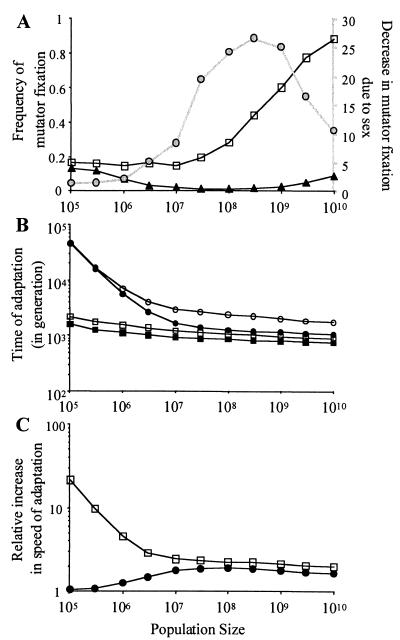
Figure 3.
Population size modifies the effect of genetic exchanges on the fixation of mutators. (A) The fixation frequency (1,000 simulations per point) of a 100-fold mutator allele, with a rate of sex of 10−4 per gene per generation (▴) or without genetic exchanges (□) as a function of the population size. The effect of sex on the fate of the mutator (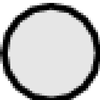 ) is the ratio of the frequency of mutator fixation without sex to the frequency of mutator fixation with sex. (B) Difference in adaptation times between mutator and antimutator backgrounds in large populations (over 200 simulations). ○, ●, The mean adaptation time of populations with a fixed low mutation rate, with a rate of sex of 10−4 per gene per generation (●) or without genetic exchanges (○). □, ■, Populations with a fixed high mutation rate (100-fold higher than the previous population) with a rate of sex of 10−4 per gene per generation (■) or without sex (□). (C) Increase in the speed of adaptation due to a mutator background or to the presence of genetic exchanges. □, The factor by which mutator background accelerates adaptation compared with nonmutator background in asexual population; ●, the factor by which genetic exchanges (at a rate of 10−4 per gene per generation) accelerate adaptation compared with asexual populations in the nonmutator background.
) is the ratio of the frequency of mutator fixation without sex to the frequency of mutator fixation with sex. (B) Difference in adaptation times between mutator and antimutator backgrounds in large populations (over 200 simulations). ○, ●, The mean adaptation time of populations with a fixed low mutation rate, with a rate of sex of 10−4 per gene per generation (●) or without genetic exchanges (○). □, ■, Populations with a fixed high mutation rate (100-fold higher than the previous population) with a rate of sex of 10−4 per gene per generation (■) or without sex (□). (C) Increase in the speed of adaptation due to a mutator background or to the presence of genetic exchanges. □, The factor by which mutator background accelerates adaptation compared with nonmutator background in asexual population; ●, the factor by which genetic exchanges (at a rate of 10−4 per gene per generation) accelerate adaptation compared with asexual populations in the nonmutator background.