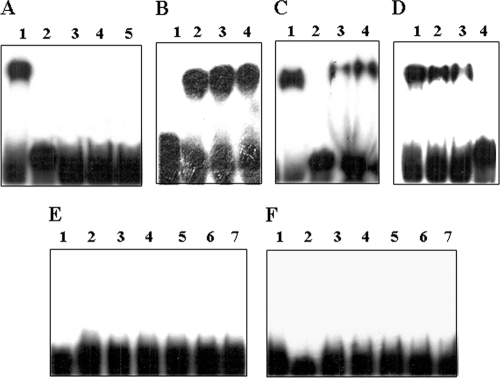
FIG. 2.
(A) Binding of CcpA, HPr, and HPr-Ser-P to 117-bp probe containing cre1-2 by electrophoretic mobility shift assay. Lane 1, 0.78 nM CcpA; lane 2, free probe; lane 3, 0.6 nM HPr; lanes 4 and 5, 0.6 nM and 1.2 nM HPr-Ser-P, respectively. (B) Binding of CcpA to 117-bp probe and competition with cold DNA. Lane 1, free probe; lane 2, 0.78 nM CcpA; lanes 3 and 4, 0.78 nM CcpA plus 200- and 400-fold excess cold probe DNA, respectively. (C) Binding of CcpA and HPr-Ser-P to 117-bp probe. Lane 1, 0.78 nM CcpA; lane 2, free probe; lanes 3 and 4, 0.78 nM CcpA plus 0.6 nM and 1.2 nM HPr-Ser-P, respectively. (D) Competition of CcpA-HPr-Ser-P complex binding to 117-bp probe with cold probe DNA. Lane 1, 0.78 nM CcpA plus 0.6 nM HPr-Ser-P; lanes 2, 3, and 4, 0.78 nM CcpA plus 0.6 nM HPr-Ser-P with 50-, 100-, and 200-fold excess cold competitor DNA, respectively. (E) Binding of CcpA, HPr, and HPr-Ser-P to probe DNA containing cre3. Lane 1, free probe; lane 2, 0.78 nM CcpA; lane 3, 0.6 nM HPr; lanes 4 and 5, 0.6 nM and 1.2 nM HPr-Ser-P, respectively; lanes 6 and 7, 0.78 nM CcpA plus 0.6 nM and 1.2 nM HPr-Ser-P, respectively. (F) Binding of CcpA, HPr, and HPr-Ser-P to probe DNA containing cre4. The lanes are as in panel E.