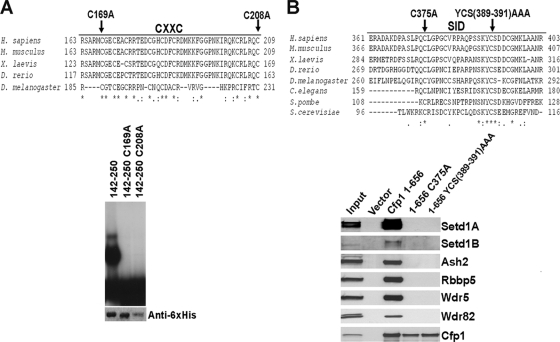
FIG. 7.
Mutations within the CXXC domain and SID of Cfp1 abolish DNA-binding activity or interaction of Cfp1 with the Setd1 complexes. (A) A multispecies alignment of the CXXC domain of Cfp1 is shown. Asterisks mark identical amino acid residues conserved between species, a colon indicates a conserved amino acid substitution, and period indicates a semiconserved amino acid substitution. The amino acids chosen for site-directed mutagenesis (C169 and C208) are indicated with arrows. As previously published (26), EMSA was performed using a CpG-oligonucleotide probe containing a nonmethylated CpG motif and wild-type or mutated Cfp1142-260 expressed as His6-tagged fusion proteins. The bottom panel presents Western blot analysis using anti-His6 antibody, demonstrating the expression and recovery of each recombinant protein. A portion of this figure was reprinted from reference 26 with permission from the publisher. (B) A multispecies alignment of the SID of Cfp1 is shown. The amino acids chosen for site-directed mutagenesis (C375 and YCS389-391AAA) are indicated with arrows. As previously published (7), FLAG immunoprecipitation was carried out using full-length wild-type or mutated Cfp1. Western blot analysis of immunoprecipitates was performed to determine interaction of Cfp1 with Setd1A, Setd1B, Ash2, Rbbp5, Wdr5, Wdr82. This figure is reprinted from reference 7 with permission from the publisher.