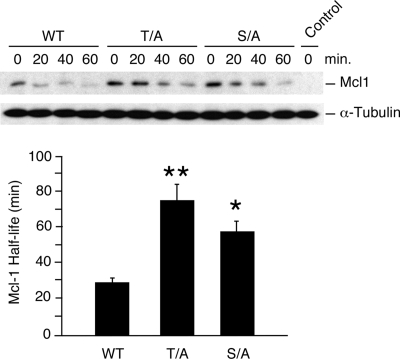
FIG. 4.
Phosphorylation is required for UV-stimulated Mcl-1 degradation. Murine Mcl-1LoxP/LoxP Gt(ROSA)26Sor-CreEsr1 fibroblasts were transduced with an mMcl-1 (wild type [WT], Thr-144Ala, or Ser-140Ala) expression vector or an empty pBABE-IRES-Puro vector (control) and selected by treatment with 2 μg/ml puromycin (2 days). The endogenous Mcl-1 gene was deleted by treatment of the cells with 1 μM 4-hydroxytamoxifen (1 day). The half-life of the mMcl-1 protein was examined following exposure of the cells to UV radiation (60 J/m2). The amounts of Mcl-1 and α-tubulin were detected by autoradiography and quantitated using a Kodak 4000MM imaging station. The half-lives of wild-type and phosphorylation-defective Mcl-1 proteins (T/A and S/A) are presented. The half-lives of the mutant proteins were significantly longer than that of wild-type Mcl-1 (mean ± SD; n = 6; *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01).