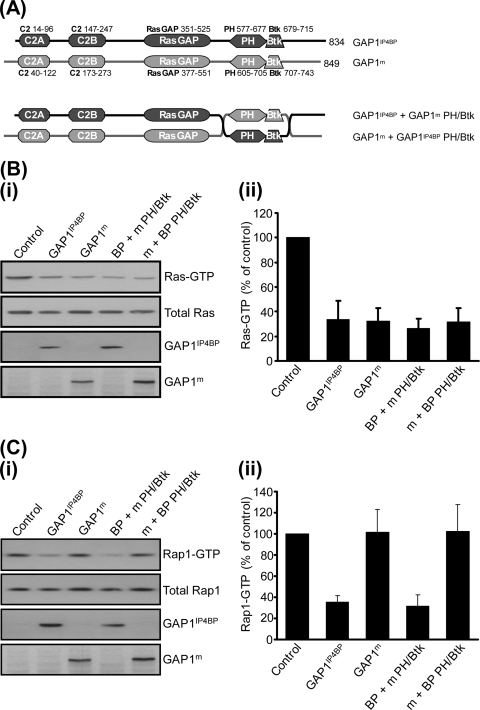
FIG. 2.
Exchange of the PH and Btk domains between GAP1IP4BP and GAP1m has no effect on the Ras and Rap GAP activities of either hybrid protein in vivo. (A) Schematic diagram of the PH/Btk domain exchange constructs used in this study. (B, part i) CHO-T cells were transiently cotransfected with 2.5 μg Ras and 1 μg of the relevant GAP1IP4BP or GAP1m expression vector. Compared to that in control cells, the amount of Ras-GTP is significantly decreased in cells expressing wild-type GAP1IP4BP and GAP1m, as well as in cells expressing the GAP1IP4BP and GAP1m PH/Btk domain hybrid proteins. (C, part i) CHO-T cells were transiently cotransfected with 2.5 μg HA-tagged Rap1A and 1 μg of the relevant GAP1IP4BP or GAP1m expression vector. Compared to that in control cells, the amount of Rap1-GTP is only significantly decreased in cells expressing wild-type GAP1IP4BP and in cells expressing GAP1IP4BP with the PH/Btk domain from GAP1m. Wild-type GAP1m and GAP1m with the PH/Btk domain from GAP1IP4BP do not display Rap1 GAP activity. Ras-GTP (B, part ii) and Rap1-GTP (C, part ii) levels from CHO-T cells are expressed as percentages of the pulldown level in control cells (average of six separate experiments ± the standard error of the mean).