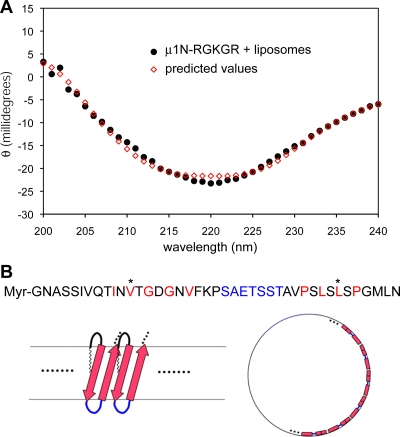
FIG. 8.
(A) CD spectrum of liposome disruption reactions. Empty liposomes were incubated with 30 μg/ml myr-μ1N-RGKGR peptide and 5% DMSO for 10 min at 37°C, then chilled on ice, and dialyzed extensively against cold PB. The spectrum of a parallel sample, containing 5% DMSO in PB without peptide, was essentially flat, and the difference spectrum of the peptide sample after subtracting the DMSO control is shown. A predicted spectrum after curve fitting using the multilinear regression algorithm (25) is superimposed. (B) Model of pore formation by μ1N. Top, amino acid sequence of μ1N, showing segments of alternating hydrophobic (red) and polar residues connected by a polar sequence (blue). The three prototype reovirus strains (T1L, type 2 Jones, and type 3 Dearing) have identical μ1N amino acid sequences. Bottom left, proposed model for μ1N insertion as a β-hairpin, with a number of such hairpins forming a β-barrel. The strands of the hairpin are shown as arrows, and the polar connector is shown as a blue loop; the limits of the hydrophobic parts of the membrane bilayer are represented by gray lines. The N-terminal myristoyl group is assumed to insert into the membrane. Bottom right, schematic en face view to illustrate the formation of a pore ∼5 nm in diameter by 14 to 16 such hairpins.