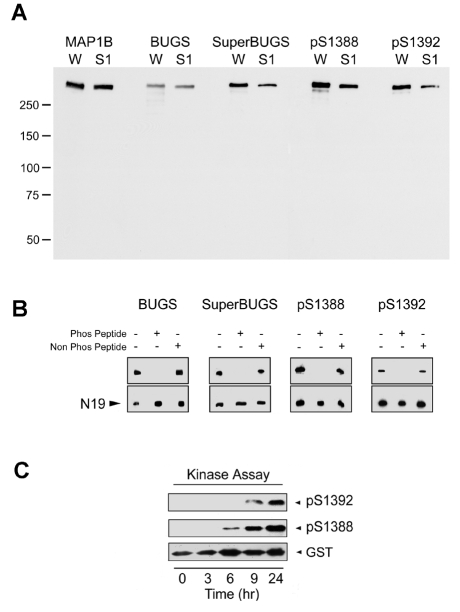
Fig. 2.
Phospho-specificity of polyclonal antibodies raised to putative sites of GSK3β phosphorylation on MAP1B. (A) Affinity-purified pAbs against mouse MAP1B S1260-P (BUGS) and S1265-P (SuperBUGS), and against rat S1388-P and S1392-P were immunoblotted against proteins from neonatal rat whole brain (W) or neonatal rat brain supernatant (S1). All of these antibodies recognise a protein that co-migrates with MAP1B (∼320 kDa), as indicated by comparison with protein bands recognised by pAb anti-MAP1B-C1, which recognises all forms of MAP1B (Johnstone et al., 1997). (B) Phospho-peptide inhibition assay. Pre-incubation of antibodies with the appropriate phosphorylated peptide (Phos Peptide) blocks antibody binding to native MAP1B, whereas non-phosphorylated peptide (Non Phos Peptide) has no effect. Lane 1, antibody alone; lane 2, antibody incubated with phosphorylated peptide; lane 3, antibody incubated with non-phosphorylated peptide. Peptide concentration was 8 μM, except for BUGS, for which 0.8 μM was used. N19, pAb against MAP1B. (C) A recombinant MAP1B protein (SP; Fig. 1) containing S1388 and S1392 was phosphorylated in an in vitro kinase assay and tested for immunoreactivity with pAbs against S1388-P and S1392-P. These pAbs only recognised the SP recombinant protein after it had become phosphorylated in the protein-kinase assay (6-9 hours), showing that these antibodies are phosphospecific. Blots were stripped and probed with an antibody against GST to show the level of SP (GST).