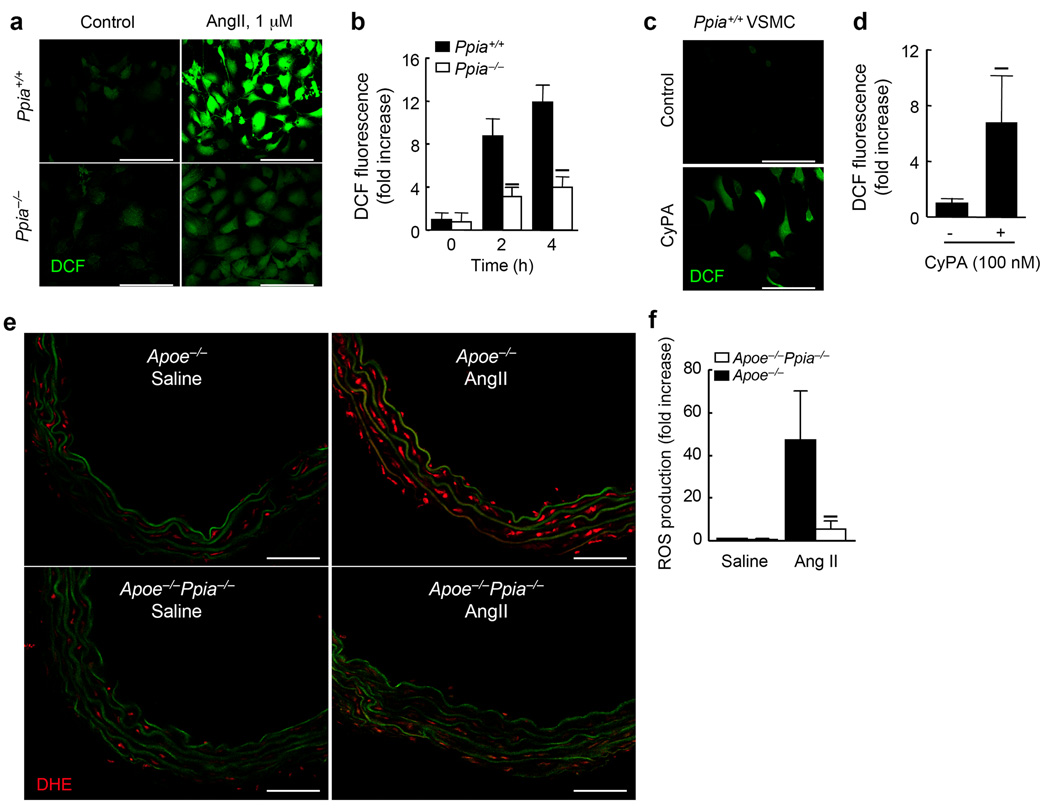
Figure 5.
AngII-induced ROS formation in VSMC requires CyPA. (a) Representative DCF staining of mouse aortic VSMC. AngII-induced ROS generation was decreased in CyPA-deficient VSMC. (b) Densitometric analysis of DCF fluorescence in response to AngII shows ~60% reduction in Ppia−/− VSMC at 4 h. Results are mean ± SD of 5 independent experiments. ★P < 0.01 compared with Ppia+/+ VSMC. (c) Representative DCF staining of Ppia+/+ VSMC in response to 100 nM CyPA. (d) Densitometric analysis of DCF fluorescence in Ppia+/+ VSMC in response to 100 nM CyPA. Results are mean ± SD of 5 independent experiments. ★P < 0.01 compared with control VSMC. (e) In situ dihydroethidium (DHE) staining of mouse aorta showed decreased DHE staining in Apoe−/−Ppia−/− aortas. Aortas from Apoe−/− and Apoe−/−Ppia−/− mice infused with saline or AngII for 7 d were analysed. Media green fluorescence is from elastin fiber autofluorescence, which appeared both in control and AngII-treated aorta. All sections are shown with the lumen above. Scale bars, 100 µm. (f) Densitometric analysis of DHE fluorescence relative to control Apoe−/− mice (saline-infused). Results are mean ± SD. ★P < 0.01 compared with Apoe−/− mice.