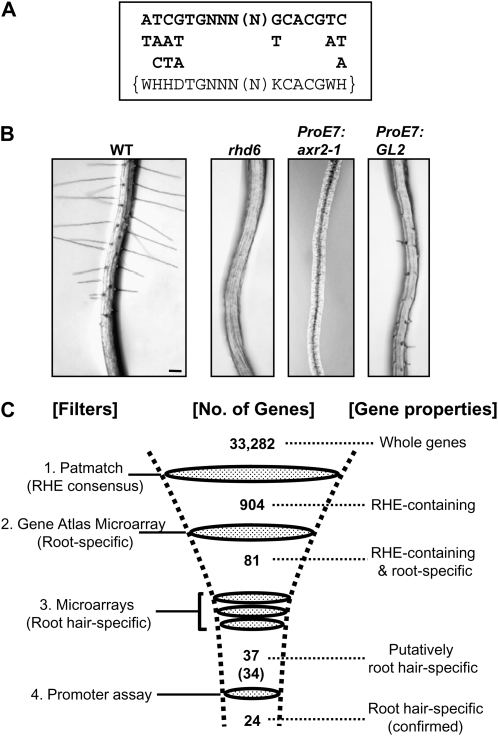
Figure 2.
Tools for screening root hair-specific Arabidopsis genes. A, The RHE consensus. The top sequence represents majority nucleotides in the RHEs from angiosperm root hair genes. The nucleotides below the sequence are the next most frequent nucleotide species. The bottom sequence inside brackets refers to the multiple nucleotide consensus from the above sequence and was used in Patmatch to screen out RHE-containing genes from the Arabidopsis genome. B, Root hair-defective Arabidopsis mutant and transgenic lines used to produce triple microarray filters for root hair specificity. The root hair-repressing genes axr2-1 and GL2 were specifically expressed in the root hair using the root hair-specific EXPA7 promoter (ProE7). Genes down-regulated in the root hair-defective rhd6 mutant or transgenic lines were identified by microarray analysis of root-expressible RNAs. WT, Wild type. Bar = 0.1 mm for all. C, Filtering of root hair-specific genes from the whole Arabidopsis genome. Four filtering steps were used to purify the root hair-specific genes: 1, Patmatch to filter RHE-containing genes; 2, Genevestigator Gene Atlas microarray database to filter the RHE-containing genes with root specificity; 3, microarray data from root hair-defective mutant and transgenic lines to filter putative root hair-specific genes; 4, experimental promoter assay of 34 putative root hair-specific genes to confirm root hair specificity, yielding 24 root hair-specific genes, among which five were previously identified.