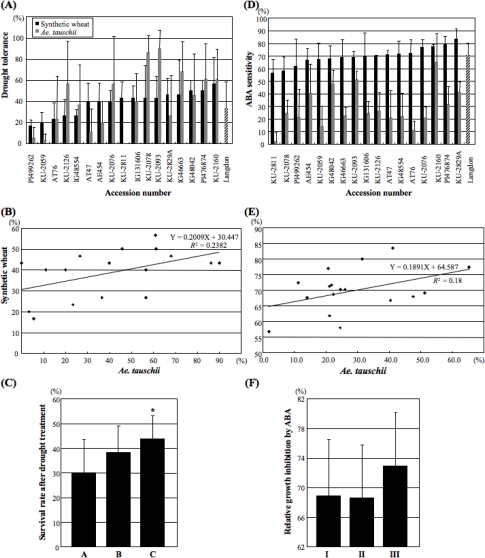
Figure 3.
Variation in drought tolerance and ABA sensitivity of 17 synthetic wheats and their parental lines.
(A) Drought tolerance revealed by survival rate after a 4 d drought treatment. (B) Scatter plot of drought tolerance in the synthetics and parental Ae. tauschii accessions. (C) Comparison of drought tolerance for three categories of synthetics having parental Ae. tauschi lines with distinct levels of drought tolerance. Student’s t-test was used to test for statistical significance (*P < 0.05) compared with the drought-sensitive group with low drought tolerance. A, drought-sensitive accessions; B, accessions with moderate drought tolerance; C, highly drought tolerant accessions. (D) ABA sensitivity based on relative growth inhibition (%) due to 20 μM ABA treatment. Means ± SD were calculated from data from three independent experiments. In each experiment, at least five plants were tested. (E) Scatter plot of ABA sensitivity in the synthetics and parental Ae. tauschii accessions. (F) Comparison of ABA sensitivity for three categories of synthetics having parental Ae. tauschi lines with distinct levels of ABA sensitivity. I, low ABA-sensitivity accessions; II, moderately ABA-sensitive accessions; III, highly ABA-sensitive accessions.