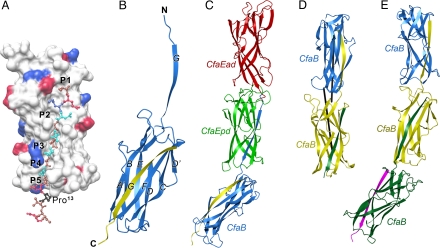
Fig. 2.
Crystal structures of CFA/I fimbrial subunits and their recombinant fusions. (A) The surface structure of the donor-strand exchanged CfaB, with the bound N-terminal extension shown in ball-and-stick format. Positively charged surfaces are shown in blue; negatively charged surfaces, in red. The 5 hydrophobic pockets in the hydrophobic groove are labeled P1 to P5. In the 16 N-terminal residues shown, hydrophobic residues are brown, polar residues cyan, and Pro13, which sits outside the groove, is shown in black. (B) Ribbon diagram of CfaB with native CfaB colored blue and the donor strand G contributed from an associating subunit in yellow. (C) Ribbon diagram of the structure of the CfaEB fusion. The 3 domains are colored in red, green, and blue, for CfaEad, CfaEpd, and CfaB, respectively. The yellow strand associating with the blue CfaB is an engineered donor strand filling the hydrophobic groove of the CfaB subunit. (D) Ribbon representation of the structure of CfaBB. The 2 associating CfaB subunits are colored blue and yellow, respectively. The green strand is an engineered donor strand. The 2 longest inertial vectors for the subunits are drawn as black rods. (E) Ribbon diagram of the structure of CfaBBB. The 3 subunits are colored blue, yellow, and green, respectively. The engineered donor strand filling the final groove is colored magenta.