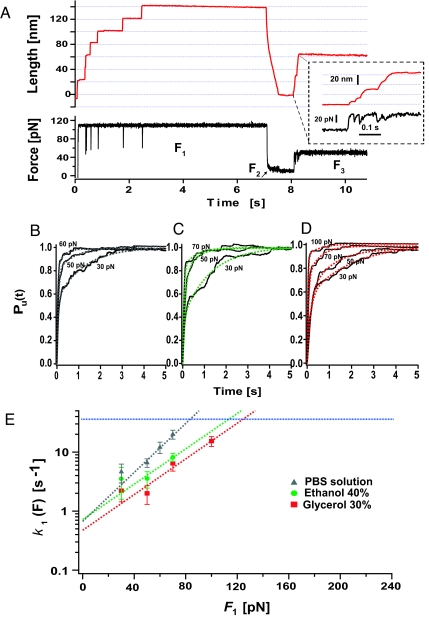
Fig. 4.
The collapsed conformations are solvent-insensitive. (A) We use the 3-pulse protocol (F1 to F3) to measure the force-dependent extension of the collapsed ensemble. After a standard force-quench sequence (F1 and F2), the force-dependent rate of extension of the collapsed conformations k1 is measured by varying F3 within the range 30–70 pN in (B) PBS aqueous solution, data from (25), (C) ethanol solution (40% vol/vol), and (D) glycerol solution (30% vol/vol). We measured the unfolding rate from the weighted average of biexponential fits to the unraveling time course of 25–50 recordings at each force. (E) We fit an Arrhenius term to k1 (F) to estimate the average size of the activation energy barrier, <ΔG1>, and distance to the transition state, <Δx1> of the collapsed conformations in PBS solution and in solutions containing 40% ethanol and 30% glycerol. The data shows that the Arrhenius fits for all 3 solvent environments converge to the same rate at 0 force, indicating that <ΔG1> is solvent-independent.