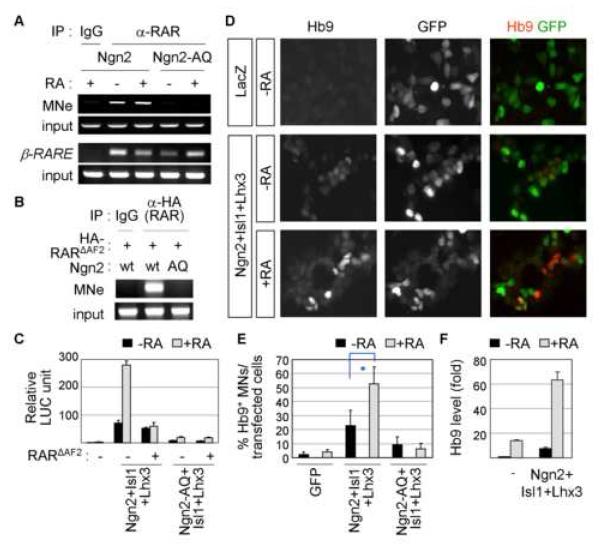
Figure 3. RA-signaling promotes the specification of a motor neuron fate by Ngn2.
(A) ChIP assays using IP with anti-RAR antibody in P19 cells transfected with Ngn2 or Ngn2-AQ. DNA-binding activity of Ngn2 is required to recruit RAR to MNe in a RA-independent manner, as shown by occupancy of MNe by RAR in the presence of Ngn2 but not Ngn2-AQ. β-RARE is a cognate DNA response element of RAR. (B) ChIP assays in P19 cells transfected with HA-RARΔAF2 and Ngn2 or Ngn2-AQ. RARΔAF2 is recruited to MNe by Ngn2. (C) RA synergizes with Ngn2 and Isl1/Lhx3 in activating MNe:LUC reporter in P19 cells. (D-F) RA stimulates motor neuron differentiation in P19 cells transfected with Ngn2, Isl1 and Lhx3, as monitored by immunostaining with anti-Hb9 antibody (D, E) and measuring Hb9 mRNA levels in quantitative RT-PCR (F). GFP+-cells mark transfected cells (D). (C, E, F) The error bars represent the standard deviation. (E) Asterisk, p<0.001 in the two-tailed t-test.