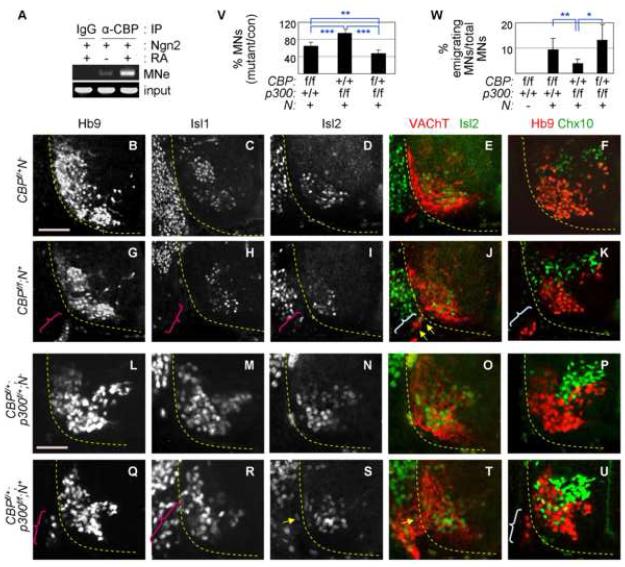
Figure 5. CBP is required for proper motor neuron development.
(A) RA facilitates the recruitment of CBP to MNe in P19 cells expressing Ngn2, as shown by ChIP using anti-CBP antibody. (B-U) Immunostaining of motor neuron markers Hb9, Isl1, Isl2, and VAChT and a V2-interneuron marker Ch×10 in E12.0 CBP mutants and E11.5 CBP/p300-compound mutants. The ventral quadrant of the spinal cord is shown. Ectopically emigrating motor neurons outside the spinal cord are marked by parentheses. These emigrating cells coexpress Isl2 and VAChT, as indicated by yellow arrows. (V) Quantification of Hb9+-motor neurons in both inside and outside the spinal cord of CBP/p300 mutants at cervical levels. The number of motor neurons of each genotype over their control littermate is shown in %. (W) Quantification of ectopically emigrating Hb9+-motor neurons outside the spinal cord in CBP/p300 mutants at thoracic levels. The number of emigrating motor neurons over the total number of motor neurons is shown in %. (V, W) One asterisk, p<0.01; two asterisks, p<0.001; three asterisks, p<0.0001 in the two-tailed t-test. The error bars represent the standard deviation. Scale bars, 100 μm (B-K), 50 μm (L-U).