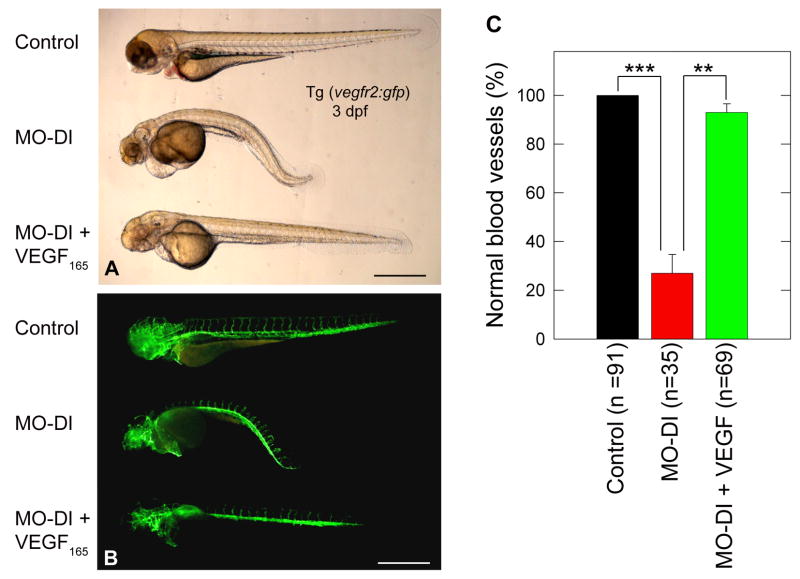
Fig. 4.
VEGF-A165 protein can rescue the morphant phenotype induced by MO-DI perlecan knockdown. Panels (A,B) are live bright field and corresponding GFP composite images of a representative control (top), MO-DI (middle) and rescue (MO-DI + VEGF-A165, bottom) sample. Note the clear rescue of both the muscle and vascular phenotype by VEGF-A165, as compared to MO-DI alone. Microinjection of VEGF-A165 alone did not result in any observable phenotype (data not shown). All images are left-side views of 3dpf Tg(vegfr2:g-rcfp) embryos with dorsal up and anterior to the left. Scale bar, 500 μm. The graph displayed in (C) represents the mean ± S.E.M. of three individual experiments, with rescue screening based upon embryos exhibiting normal vascular development (**P<0.01; ***P<0.001).