Figure 6.
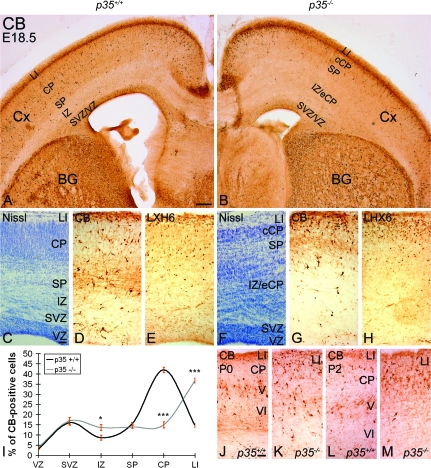
Abnormal accumulation of cortical interneurons in LI and IZ of p35−/−mice. (A, B) E18.5 coronal forebrain sections labeled for CB. CB+ cells are mainly found in the upper part of the cortex, in zones LI/CP/SP, and only rarely in the IZ, in both p35+/+ (A) and p35−/− (B) mice. (C) Cortical layers are clearly delineated in Nissl-stained sections of p35+/+ mice. (D, E) CB+ and LHX6+ cells are found evenly distributed within LI, CP, and SP layers. (F) In Nissl-stained p35−/− cortex, CP is thinner and the IZ as well as LI appear thicker and cell dense compared with controls. (G, H) CB+ and LHX6+ cells, although present in all developing layers, are mostly accumulated in LI. Normal position and cell content of the SVZ interneuron stream is found in both genotypes. (I) Relative distribution of CB+ cells in the cortex (mean percentage ± SEM). Error bars represent SEM. A significant difference in layer distribution of CB+ (P < 0.05, χ2 test) cells in the cortex is observed between p35+/+ and p35−/− mice. Bin comparison is done by Student's t-test (*P < 0.05, ***P < 0.005). (J–M) The positions of CB+ cells in the early postnatal (P0 and P2) cortex differ between the genotypes. In controls, they are mostly in layer V (J, L), contrasting with the upper cortex, including LI, in p35−/− mice (K, M). Cx, cortex; BG, basal ganglia; VZ, ventricular zone. Scale bars, 500 μm (A, B); 100 μm (C–H); 50 μm (J–M).