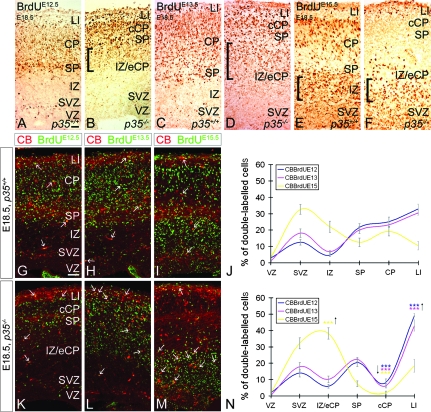
Figure 8.
Abnormal distribution of early- and late-born pyramidal cells and interneurons in embryonic p35−/− mice. Pregnant dams received a single BrdU injection at E12.5, E13.5, or E15.5 to label early or late-born cortical cells. Coronal sections of E18.5 cortices labeled for BrdU and BrdU/CB. In both p35+/+ and p35−/− mice, early-born cells are mostly present in the LI/CP/SP layers (A–D). In p35−/− mice, these cells are also found trapped in the IZ (square brackets; B, D). Late-born cells, in control mice, migrate into the CP but fail to position themselves in the cCP in p35−/− mice; note BrdU+ cells in the IZ of both genotypes (square brackets; E, F). (G–I, K–M) Early- and late-born CB+ cells are present in all layers of both genotypes (arrows). The relative distribution of CB+/BrdU+ cells in the cortical layers of p35+/+ (J) and p35−/− (N) is presented as mean percentage ± SEM. In control mice, early- and late-born CB+ cells enter the CP and are distributed evenly (J). Many late-born CB+ cells also populate the SVZ (J). In p35−/−, few CB+/BrdU+ cells are present in the cCP and are arrested in LI (mostly early born) and in the IZ (mainly late born) compared with controls (N). Error bars represent SEM. A significant difference in layer distribution of CB+/BrdU+ (E12.5, P < 0.05; E13.5, P < 0.025; E15.5, P < 0.001; χ2 test) cells in the cortex is observed between p35+/+ and p35−/− mice. Bin comparison is done by Student's t-test (***P < 0.005). VZ, ventricular zone. Scale bar, 100 μm.