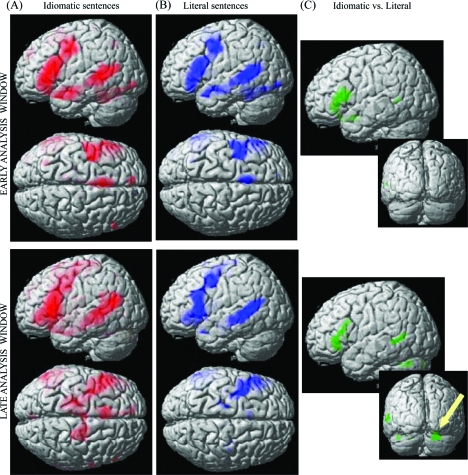
Figure 3.
Cortical activation during silent reading of (a) idioms and (b) literal sentences (P < 0.001, uncorrected), compared with the baseline (hash-marks strings), in the early (top panel) and late analysis windows (bottom panel). Results are rendered on a standard brain surface. Specific activations for the direct contrast between idioms and literal sentences are reported for both windows in (c). The inset in (c) highlights the specific activation observed in the right cerebellum for idioms, compared with literal sentences, in the late window (bottom panel).