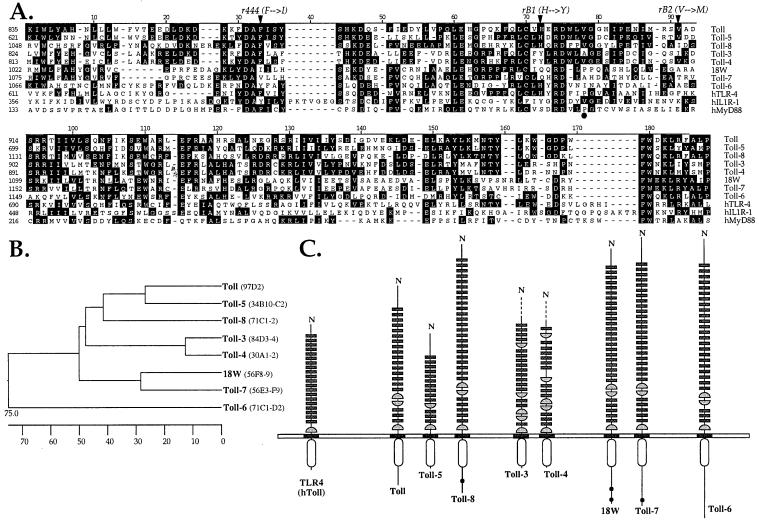
Figure 1.
The Drosophila Toll family. (A) Alignment of the TIR domains from Drosophila Toll-related molecules and human TLR4, IL-1 receptor type I (IL-1RI), and MyD88. Sequences were aligned by using the clustal method. Conserved residues are shaded in black. Residues affected in the loss-of-function r444, rB1, and rB2 alleles of Toll are indicated by arrowheads (46). The black dot points to the position of the Pro residue critical for TLR4 signaling. (B) Phylogenetic relationship between Drosophila Toll molecules based on the alignment shown in A and generated by the neighbor-joining method. The scale beneath the tree measures the distance between the sequences. The chromosomal localization of the Toll-related genes is indicated (Right). (C) Schematic representation of domain organization of Drosophila Toll-related molecules and human TLR4. The receptors are grouped according to conservation of their TIR domains. The leucine-rich repeats are indicated by small rectangles, whereas cysteine-rich carboxyl-flanking motifs and cysteine-rich amino-flanking motifs are represented by half-circles. Black dots indicate polyglutamine stretches. Incomplete sequences of Toll-3 and Toll-4 are indicated by dashed lines.