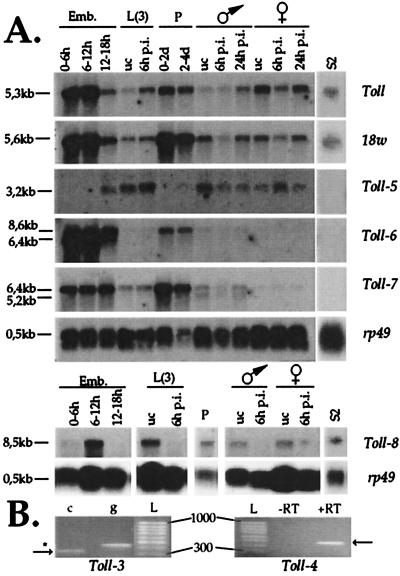
Figure 2.
Northern blot and RT-PCR analysis of Toll-related gene expression. (A) Poly(A)+ RNA extracted from embryos (Emb.), third-instar larvae [L(3)], pupae (P, 0–2 or 2–4 days), adult male or female Drosophila, and the cell line S2 were submitted to Northern blot analysis and hybridized to probes derived from Toll, 18w, and Toll-3 to Toll-8 gene sequences. No signal could be observed for the Toll-3 and Toll-4 probes. A probe recognizing RNA coding for ribosomal protein 49 (rp49) was used to ensure that comparable amounts of RNA were loaded in all lanes. uc, unchallenged; p.i., postinfection with a mixture of Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria; and d, days. (B) RT-PCR analysis of Toll-3 and Toll-4 expression. Primers specific for the Toll-3 gene were designed to flank a 104-bp intron sequence in the genomic DNA, resulting in the amplification of a 342-bp cDNA (c)-derived fragment (arrow) or a 446-bp genomic DNA (g)-derived fragment (*). Primers for the Toll-4 gene were designed to amplify a 480-bp intronless fragment. In this case, RT was omitted in a control reaction to ensure that the amplified band is derived from RNA. cDNA was prepared from mRNA derived from pupae (Toll-3) or third-instar larvae (Toll-4). L, 100-bp ladder.