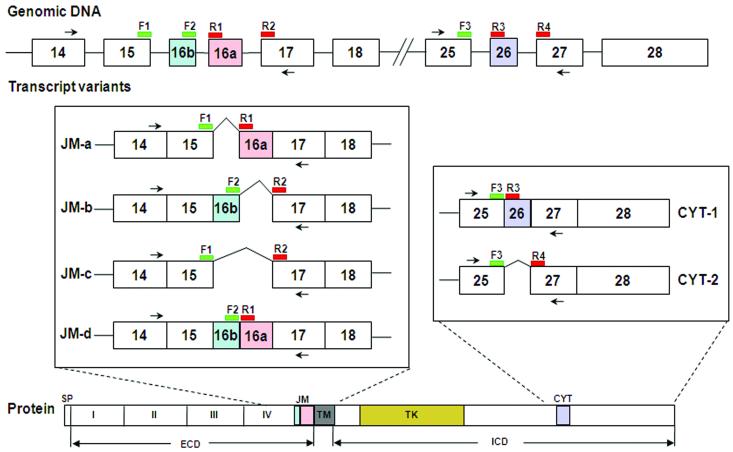
FIGURE 1.
Schematic representation of part of the exon structure of ERBB4 mRNA around the JM and CYT regions, and the design of LightCycler hybridization probes for detecting the expression of alternatively spliced variants. Two primer pairs, PC2338-PC5221 and PC5268-PC5269 (shown by black arrows in the figure) that flank the JM and CYT variable regions, respectively, were used to amplify all the JM and CYT related variants of ERBB4. For quantitative analysis of each JM variant, two donor probes, F1 and F2, were designed according to the 3′end sequences of exon 15 and exon 16b respectively and two acceptor probes, R1 and R2, were designed to match the 5′end sequences of exon 16a and exon 17 respectively. Thus, the dual-labelled probe pair F1-R1 can specifically detect the JM-a variant, while F2-R2 detects JM-b, F1-R2 detects JM-c and F2-R1 detects JM-d. For CYT variant analysis, one donor probe (F3) homologous to the 3′ end sequence of exon 25 and two acceptor probes (R3 and R4) matching 5′end sequences of exons 26 and 27 were used to generate probe pair F3-R3 for CYT-1 and F3-R4 for CYT-2. The donor probes (F1, F2 and F3) were labelled with 3′ Fluorescein. The acceptor probes (R1, R2, R3 and R4) were labelled with 5′ LightCycler Red 610 or 640 fluorescent dyes and the 3′ hydroxyl groups were blocked with a phosphate to prevent Taq DNA polymerase extension. To avoid any steric problems between the donor and acceptor fluorophores on a probe pair, a gap of 1 to 5 nucleotides (4 to 25Å distance) was designed to separate the two probes from each other. During the annealing step of real-time PCR, the PCR primers and the LightCycler probes hybridize to their specific target regions causing the donor dye (on the F probe) to come into close proximity to the acceptor dye (on the R probe). When the donor dye is excited by light from the LightCycler instrument, energy is transferred by Fluorescence Resonance Energy Transfer (FRET) from the donor to the acceptor dye. The energy transfer causes the acceptor dye to emit light at a longer wavelength which can be detected by the LightCycler instrument’s optical unit. The increase in measured fluorescent signal is directly proportional to the amount of accumulating target DNA and can therefore be used for real-time quantitative PCR analysis. SP: signal peptide; I-IV: extracellular domains I-IV; TM: transmembrane domain; TK: tyrosine kinase domain; CYT: cytoplasmic region; ECD: extracellular domain; ICD: intracellular domain.