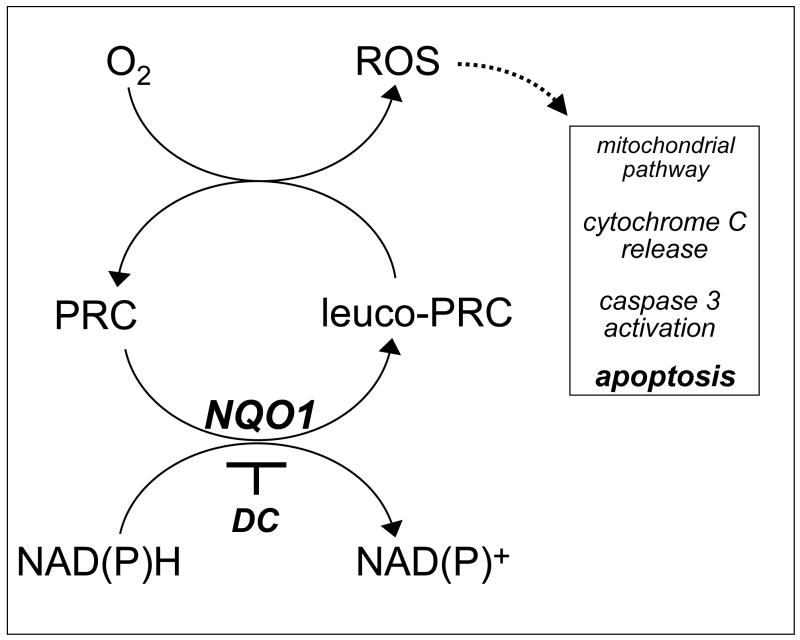
Figure 7. PRC compounds as potential redox chemotherapeutics for the targeted induction of cancer cell apoptosis.
PRC compounds may selectively target cancer cells with high NQO1 enzymatic activity by oxidative-stress dependent induction of the mitochondrial pathway of apoptosis. In this model, NQO1-dependent bioreductive activation is followed by spontaneous electron transfer between reduced PRC leuco-form and molecular oxygen leading to intracellular ROS formation with regeneration of the oxidized PRC dye-form. Consistent with this model, NQO1-inhibition by dicoumarol (DC), antioxidant intervention by catalase, and caspase inhibition by zVADfmk suppress PRC-induced apoptosis in human G361 melanoma cells. See discussion for detailed explanation.