Fig. (2).
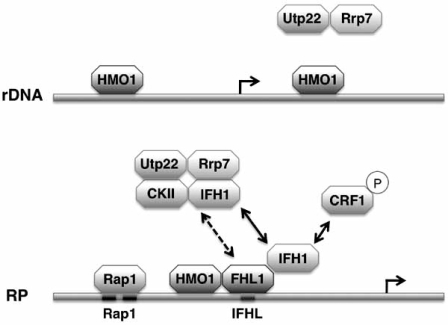
HMO1 associates with both rRNA and RP gene promoters to coordinate gene expression in response to TORC1 activity. On rDNA, HMO1 associates with both promoter and coding regions of transcriptionally active rDNA. Proposed functions include a role akin to that reported for mammalian UBP in transcriptional initiation and a role in coordinating transcriptional elongation with pre-rRNA processing, to which Utp22 and Rrp7 contribute. On most RP gene promoters, Rap1 sites are further upstream than on other Rap1-dependent genes, and association of Rap1 appears to be required for the subsequent cooperative binding of HMO1 and FHL1 at IFHL sites. When TORC1 is active, the coactivator IFH1 binds FHL1 to activate RP gene transcription. When TORC1 is inactive, phosphorylated CRF1 translocates to the nucleus to compete with IFH1 for binding to FHL1 and repress transcription. IFH1 is found in the “CURI” complex also containing Utp22, Rrp7, and CKII, with which FHL1 also associates. HMO1 dissociates from both classes of genes on inactivation of TORC1.