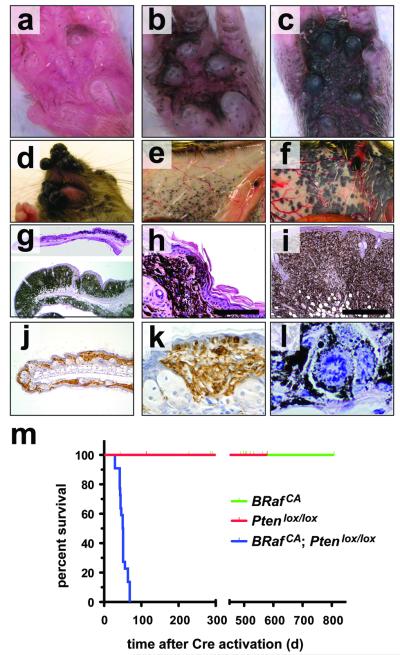
Figure 2. BRafV600E cooperates with Pten loss in the induction of malignant melanoma.
(a-c) Tyr::CreER; BRafCA/+; Ptenlox5/lox5 mice were treated topically on the paw with 4-HT to elicit BRafV600E and to silence Pten expression. The presence of pigmented lesions was assessed 6 (a), 8 (b) and 10 (c) days following 4-HT administration.
(d) Tyr::CreER; BRafCA/+; Ptenlox4-5/lox4-5 (i) were treated topically with 4-HT on the right ear. Mice were monitored for 7 weeks.
Tyr::CreER; BRafCA/+; Pten+/+ (e) and Tyr::CreER; BRafCA/+; Ptenlox4-5/lox4-5 (f) were treated topically with 4-HT on the right flank. Mice were euthanized at ∼7 weeks with the presence of malignant melanoma lesions assessed by visual inspection of the underside of the ventral/lateral skin.
Tyr::CreER; BRafCA/+; Ptenlox5/lox5 mice were treated topically on the ear, flank and tail with 4-HT. 25 days later mice were euthanized, skin sections were prepared, stained with hematoxylin and eosin and examined for the presence of pigmented cells. Almost confluent proliferation of densely pigmented cells was observed in the ear and skin (g) that penetrated deep into the dermis and the subcutis (h & i) and showed signs of pagetoid spread into the epidermis (h & k). Cells in these lesions stained positive with α-PEP1 antisera that detects expression of Tyrp1 (j & k). Pigmented cells in the lesions displayed histological characteristics of malignant melanoma, including marked cytological atypia, prominent nucleoli and aberrant mitotic figures (l)
(j) Kaplan-Meier survival analysis of 4-HT treated Tyr::CreER; BRafCA/+; Pten+/+ (n=22), Tyr::CreER; BRaf+/+; Ptenlox4-5/lox4-5 (n=5) and Tyr::CreER; BRafCA/+; Ptenlox4-5/lox4-5 (n=22) mice. Log rank tests of survival plots of the data indicated a statistically significant difference between the following survival curves: Tyr::CreER; BRafCA/+; Pten+/+ versus Tyr::CreER; BRafCA/+; Ptenlox4-5/lox4-5 (p<0.0001) and; Tyr::CreER; BRaf+/+; Ptenlox4-5/lox4-5 versus Tyr::CreER; BRafCA/+; Ptenlox4-5/lox4-5 (p<0.0002)