Figure 1.
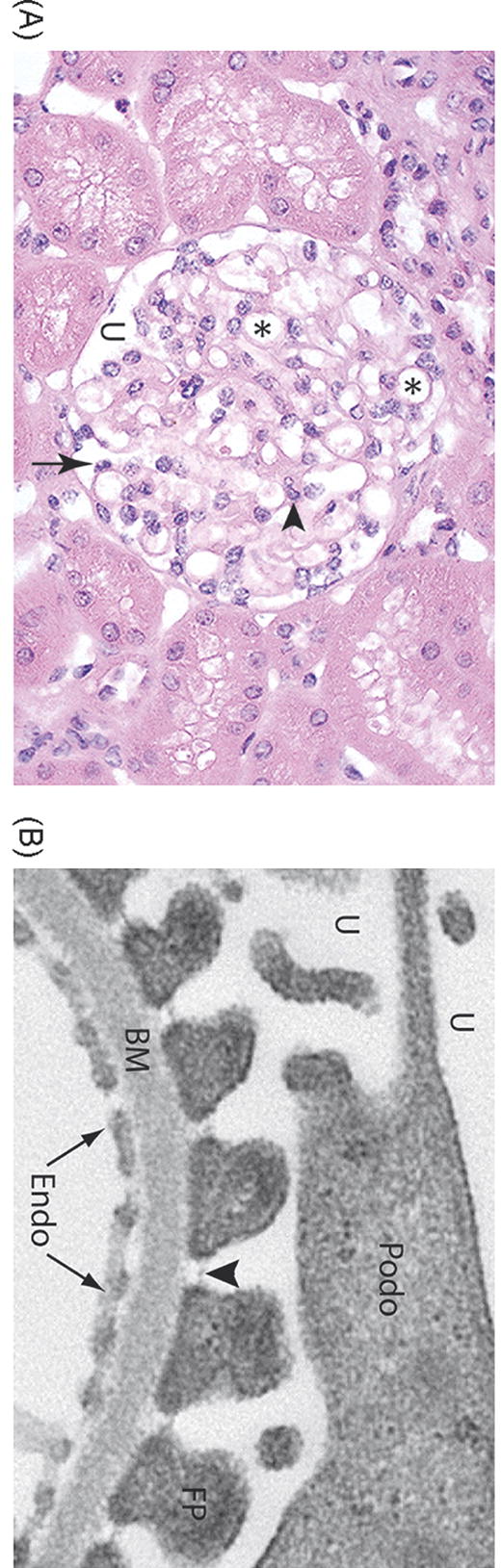
Structure of the glomerulus. A. Light micrograph of a normal glomerulus. The glomerulus consists of a tuft of capillary loops (*), which are situated within Bowman’s capsule. The capillaries are covered on the urinary space (U) by specialized glomerular epithelial cells, also known as podocytes (arrow). Mesangial cells and their associated matrix (arrowhead) provide further structural support. B. Electron microscopy of the glomerular filtration barrier of the kidney. The capillary lumen is lined by fenestrated endothelial cells (Endo), which sit atop a specialized basement membrane (BM). Podocytes (Podo) project interdigitating foot processes (FP) which attach to the basement membrane. The intercellular adhesion complex formed between adjacent foot processes is termed the slit diaphragm (arrowhead).
