Fig. 1.
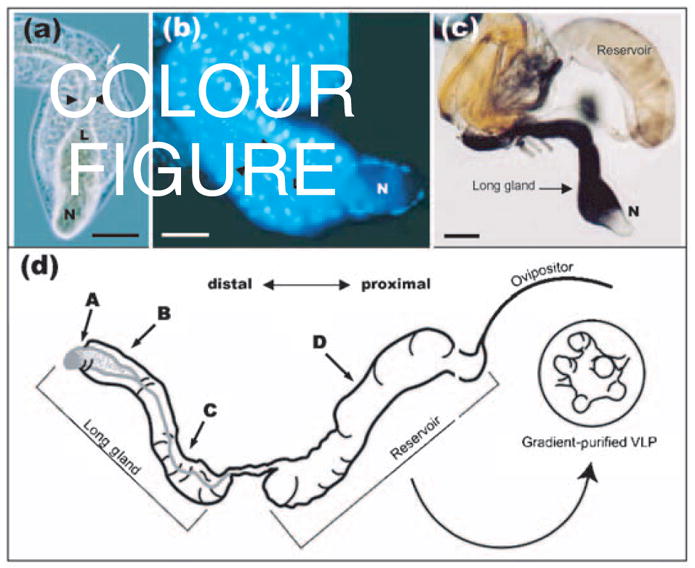
(a, b) Phase-contrast (a) and Hoechst-stained (b) micrographs showing the morphology of the L. heterotoma long gland. Arrows point to secretory cells and arrowheads to the lumen (L). Note that the lumen expands into the ‘nose’ (N) and is surrounded by a thin layer of smaller cells known as the intimal layer. Bars, 100 μm. (c) Indirect immuno-detection of p40 protein in the long gland–reservoir complex of L. heterotoma using anti-p40 antibody. Anti-p40 antibody (70 ng ml−1) was detected by a secondary antibody linked to alkaline phospha-tase (diluted 1: 1000; Promega), giving a purple reaction product. The long gland shows strong staining, whilst the reservoir shows weaker staining. Bar, 200 μm. (d) Schematic representation of the long gland–reservoir complex indicating the positions from where sections were prepared for immuno-EM in Figs 4 and 5.
