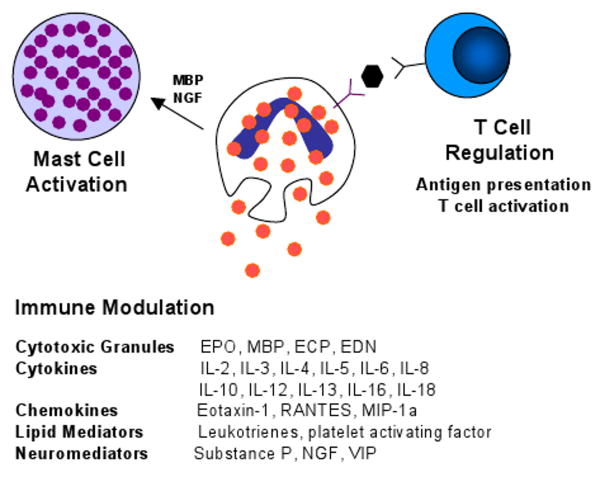
Figure 2.
Schematic diagram of an eosinophil and its multifunctional effects. Eosinophils release their preformed cytotoxic granules in response to diverse stimuli. In addition, eosinophils can modulate and perpetuate immune responses through the release of a variety of cytokines, chemokines, lipid mediators and neuromediators. Eosinophils regulate T cell activation via antigen presentation and cytokine production and activate mast cells through effects of MBP and NGF.