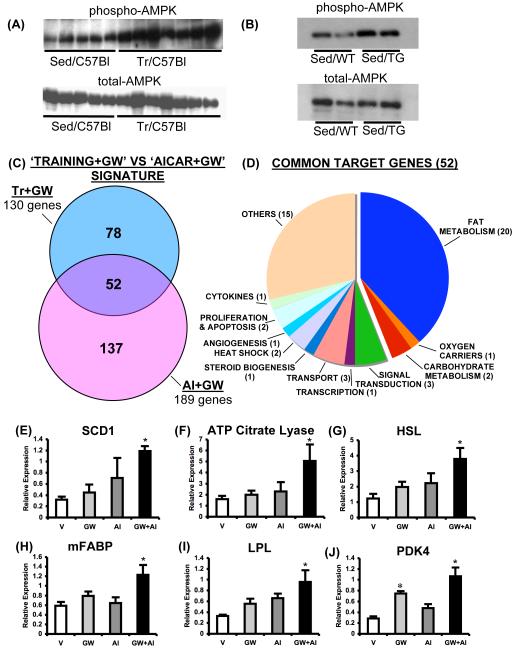
Figure 4. Synergistic regulation of muscle gene expression by PPARδ and AMPK.
(A) and (B) represent AMPK activation by exercise and VP16-PPARδ over-expression, respectively, in skeletal muscle. (C) Comparison of Tr+GW and AI+GW dependent gene signatures in quadriceps (N=3). The selection criteria used is similar to one used in Figure 3C. (D) Classification of 52 targets that were common to Tr+GW and AI+GW gene signatures. Expression of Scd1 (E), ATP citrate lyase (Acly) (F), HSL (Lipe) (G), Fabp3 (H), Lpl (I) and Pdk4 (J) transcripts in quadriceps of mice treated with vehicle (V), GW1516 (GW, 5mg/kg/day), AICAR (AI, 250 mg/kg/day) and the combination of the two drugs (GW+AI) for 6 days. Data is presented as mean±SEM (N=6). * Indicates statistically significant difference between V and indicated groups (p<0.05, One Way ANOVA; post hoc: Dunnett’s Multiple Comparison Test).