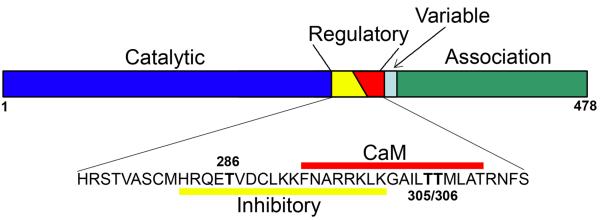
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of domain structures of αCaMKII. The protein may be divided into four functional domains, including the catalytic domain, the regulatory domain, a variable segment that differs between CaMKII isoforms, and the association domain. The regulatory domain is further divided into the autoinhibitory domain and Ca2+/calmodulin (CaM)-binding domain. CaMKII may be autophosphorylated at three threonine residues. Autophosphorylation at threonine 286 (T286) allows the kinase to retain catalytic activity even after Ca2+ concentration has returned to basal level, whereas autophosphorylation at T305 and T306 blocks subsequent activation of the kinase by Ca2+/calmodulin.