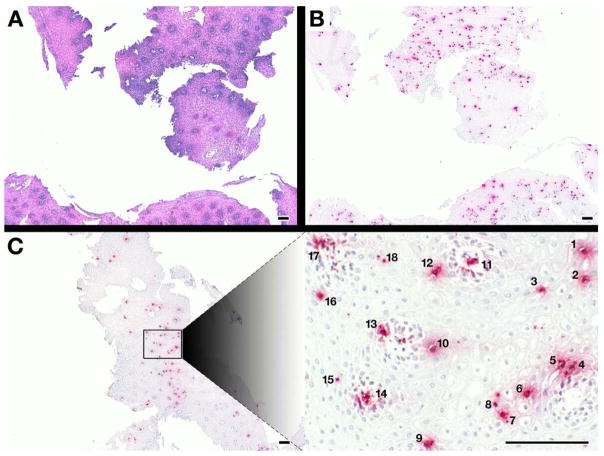
Figure 1. EPX-mAb based immunohistochemistry provides an efficient and rapid strategy to identify intact eosinophils infiltrating biopsies from eosinophil esophagitis patients.
A comparison of low (5×, 20mm2 field of view) power microscopy of (A) hematoxylin-eosin stained sections and (B) serial sections of the same patient following EPX-mAb based immunohistochemistry demonstrated that this immunohistochemical strategy easily permits the identification of infiltrating eosinophils in multiple biopsies within the field. (C) EPX-mAb based immunohistochemistry permits a rapid evaluation for the presence of intact infiltrating eosinophils of entire esophageal biopsies and the location of focal areas of eosinophil accumulation. The insert photograph in this panel is a high (40×, 0.29mm2 field of view) power field that was quickly/efficiently identified as a focal area of eosinophil accumulation (identified eosinophils are numbered 1–18) without the need of laborious time-consuming cell differential analyses. Scale bar = 100 μm.