Figure 9.
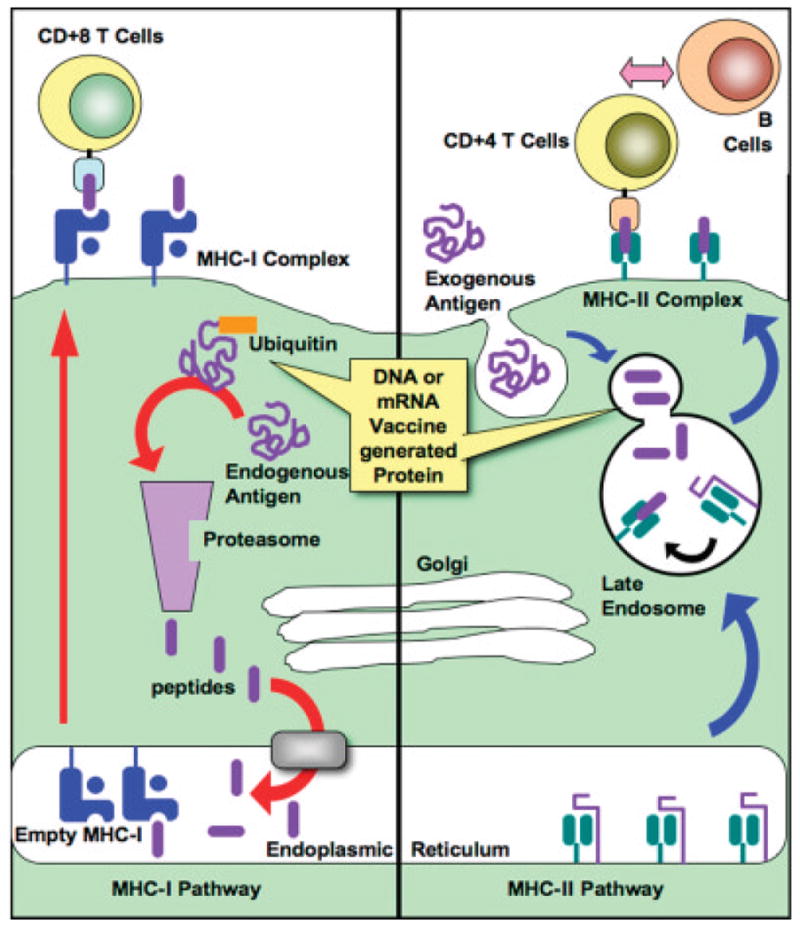
Antigen presentation and pathways of vaccine response. Plasmid DNA or mRNA is taken up by dendritic cells for intracellular expression of antigen. Antigen can be secreted (not shown) and subsequently taken up by another DCs as an exogenous antigen. Antigen expressed intracellularly by a dendritic cell or taken up through cross-priming is presented by MHC-I to CD8+ T-cells (cytotoxic leukocytes; CTLs). Antigen taken in exogenously or directed by DNA or mRNA trafficking signals are processed by the MHC-II pathway and presented to CD4+ TH cells, which can subsequently secrete: soluble cytokine signals (e.g., IL-12) back to the dendritic cell, proliferative signals (e.g., IL-2 and IFN-γ) to Tc cells, or signals directed toward B-cells (e.g., IL-4) to induce B-cell proliferation and antibody secretion.
