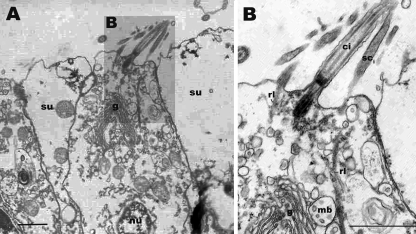
Fig. 4.
Stereocilia on the apical cell surface of oral ectodermal cells in Aurelia sp. 1. a An electronmicroscopic section of the apical surface of epidermal cells in the oral ectoderm. The apical surface is to the top. b A magnified view of the apical region of a cell in a, showing dense filaments of stereocilia (sci) extending into the cytoplasm of the cells forming rootlets (rl). Note the apparently coordinated bending of the cilium (ci) and stereocilia (sci) in a. Multivesicular bodies (mb) are seen in the apical region closely associated with the Golgi apparatus (g) (b). Similar features were previously reported from touch plate hair cells of Aurelia ephyra (Spangenberg et al. 1996). rl rootlet, mb multivesicular bodies, g Golgi, ci cilium, sci stereocilium, su supporting cell, nu nucleus