Figure 1.
Cytoplasmic Dynein Motor Domain of D. discoideum
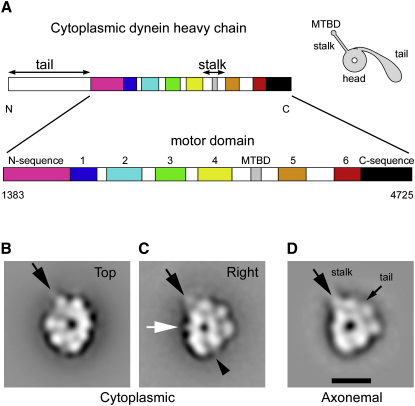
(A) Heavy-chain sequence diagram showing six AAA+ modules (numbered), N and C sequences, and the MT-binding domain (MTBD). On the right, the cartoon shows the stalk-head-tail architecture of dynein (tail formerly known as the stem).
(B and C) Negative-stain EM and single-particle image processing of the motor domain reveals two characteristic appearances: top and right views.
(D) Right view of axonemal dynein-c from Chlamydomonas reinhardtii (modified from Burgess et al., 2003) for comparison.
The point of emergence of the coiled-coil stalk (B–D, black arrows) and the tail of dynein-c (D, small arrow) are indicated, as well as a spike (C, white arrow) and stain-filled groove (C, black arrowhead) seen in cytoplasmic dynein (compare with D). The scale bar represents 10 nm.