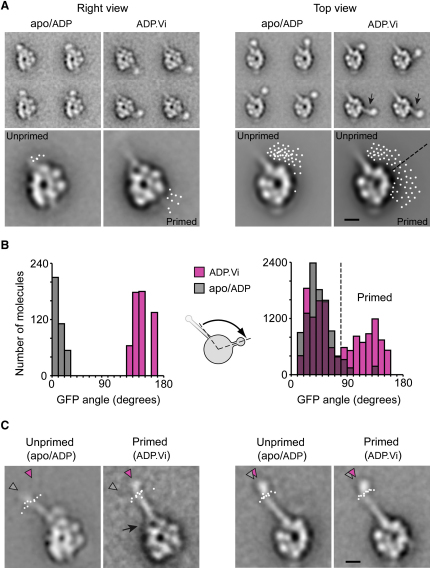
Figure 5.
Structural Changes between Unprimed and Primed Conformations
(A) Motor tagged with GFP at the N terminus and BFP at the B1 site in apo/ADP and ADP.Vi states. Small panels: representative class averages showing N-terminal GFP and distal linker (arrows). Larger panels: GFP positions detected automatically (white spots). In ADP.Vi-motors in top view, GFP positions are segregated into primed and unprimed positions (dashed line; see B).
(B) Histograms showing angular position of N-terminal GFP measured clockwise relative to an axis passing through the head center and the base of the stalk (cartoon). Mean GFP angle in right view is 10° ± 11° (n = 375) in apo/ADP compared to 145° ± 11° (mean ± SD, n = 557 molecules) in ADP.Vi. Gaussian fits to the top-view data in ADP.Vi give two peaks for GFP angles of 41° ± 18° (mean ± SD) and 124° ± 25°, which intersect at 80° (dashed line). The low-angle peak coincides with that of unprimed motors (also 41° ± 18°). The numbers of molecules in top views are 9,964 (apo/ADP) and 13,527 (ADP.Vi).
(C) Average stalk angles show a clockwise tilt between unprimed and primed motors (gray and magenta arrowheads, respectively). Stalk angles: right view: unprimed −16° ± 9° (mean ± SD, n = 3858 molecules), primed 0° ± 8° (n = 526); top view: unprimed −6° ± 6° (n = 1604), primed −4° ± 6° (n = 1667). White spots show positions of distal coiled coil in each of the ten classes used to obtain these values (see also Movie S3). Bifurcation of the stalk is indicated (arrow). Right-view unprimed motor is tagged with BFP at the B2 site rather than at the B1 site. The scale bars represent 5 nm.