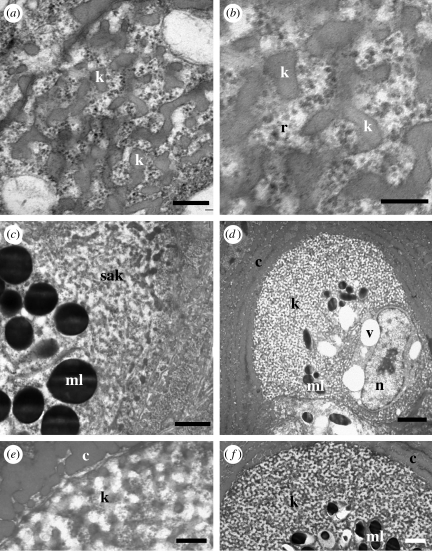
Figure 7.
Development of spongy medullary feather β-keratin. (a,b) Emergence of curved bars of spongy β-keratin within granular electron-dense materials including ribosomes. (c) Region of self-assembling β-keratin above an aggregation of melanosomes. (d) Medullary cell with extensive spongy β-keratin peripheral to an array of melanosomes. Cytoplasmic voids are greatly reduced and the nucleus is visible again. Keratin between the voids and the melanosomes is not completely assembled. (e,f) Mature spongy β-keratin in final stages of assembly. Distances from the base of the feather germ: (a–f) 7.5 mm. Scale bars: (a,e) 300 nm, (b) 200 nm, (c) 600 nm, (d) 2 μm, and (f) 1 μm. b, barbule cell; c, cortical cell; k, spongy β-keratin; ml, melanosome; n, nucleus; r, ribosome; sak, self-assembling keratin; v, cytoplasmic void.